What is Diabetes?
(This is a long article)
Diabetes got its name from the sweet taste of the urine of diabetics. In distant days the medics of old were forced to taste the urine to detect the presence of diabetes. In diabetics, the urine is sweet because of the presence of large amounts of sugar. This occurs because the cells in the body are no longer able to absorb sugar brought to them by the blood. Sugar then accumulates to such high levels that it appears in the urine in large amounts. This is diabetes.
What makes the cells unable to absorb sugar?
There is a substance called insulin which performs many functions in the body. It is produced by the pancreas, a curved slender organ placed just behind the stomach. The special function of insulin is to help transport molecules of glucose (sugar) from the blood stream into the cells, especially muscle cells. When there is little or no insulin, or when the available insulin cannot be used, these cells cannot absorb insulin and are starved of energy.
Why does this cause problems in the body?
In the first place, muscle cells are starved of their main energy source. When muscles cannot work properly, lethargy and weakness will follow. However a more important cause of weakness and fatigue in diabetics is loss of fluids and important salts from the body in the urine. In order for the kidneys to get rid of the large amounts of sugar in the urine, lots of water is used to dissolve the sugar. When this water is lost from the body unfortunately it is accompanied by loss of significant amounts of important salts like sodium chloride, potassium, bicarbonate and others. This produces two effects in the body - dehydration (loss of fluid) and metabolic imbalances. These can be serious enough to cause coma and death if they continue long enough.
How will my diabetes be treated?
The main aim of any treatment of diabetes is to reduce the level of glucose in the blood stream, by encouraging the muscle cells to resume absorbing it. There are many ways of treating diabetes, a combination of which will be used in virtually all diabetics.
Lifestyle Changes
All diabetics can benefit from lifestyle adjustments, no matter what other measures are being used to treat their diabetes. The two most important lifestyle changes involve DIET and EXERCISE.
DIET is important simply because many diabetics are overweight. Despite what many persons think, being overweight has one and only one simple cause - overeating. Overeating is related to the energy needs of your body, which in turn are related to your energy output. A simple equation will make this clear:
Food intake = Energy output + / - stored fat
This simply indicates that the caloric value of the food you eat has only two fates in the body:
- produce energy for work, exercise etc
- any excess energy is stored as fat
On the other hand if there is not enough energy to satisfy your energy demands, fat is broken down to produce energy.
The aim of dieting is to supply the body with somewhat LESS energy than is required. This then forces the body to break down fat (stored energy from the past) to supply the extra energy. The result of this is that you lose weight. Weight loss by itself can have a dramatic and beneficial effect on the management of diabetes.

EXERCISE
...is the other very important change many diabetics can make to assist in the management of their condition. You should first check with your doctor to verify that you are in a fit condition for exercise. However with few exceptions almost everybody can walk; if you are otherwise healthy, especially if your diabetes is mild, then swimming, jogging and gentle sports can markedly improve your health. A look at the equation above shows that the effect of exercise is to make less food energy available for conversion into fat. Alternatively, exercise can accelerate the rate at which stored fat is broken down to produce energy.
When exercise and diet control are combined, one can derive the maximum benefit. Often in early diabetes, this combination may be THE ONLY TREATMENT needed.
DRUGS
While diet and exercise play very important roles in the management of diabetes, many diabetics sooner or later will require drug treatment. There are a few major kinds of diabetic tablets, all of which either stimulate the pancreas to produce more insulin, or encourage the body's cells to absorb insulin more efficiently.
If you are taking tablets for diabetes, it is important to understand a few facts:
- Always take your medication as prescribed by the doctor
- Do not forget to take your tablets
- Do not double up (take a double amount) if you happen to miss a day
- Don't miss meals; if you anticipate that a meal will be late, take a snack with you
- Don't take anyone else's tablets, even if you are sure they look like yours
- Don't "run out" of medication. Always restock when you have a week's medication left.
One very important caution is to avoid the well-meant but often misguided advice of the many friends and acquaintances who will urge you to try this and that. All countries have their folklore regarding disease, and Barbados is no exception. However many of these nostrums and concoctions have absolutely no proven worth in combating diabetes.

If your diabetes cannot be managed by tablets, you will need to take insulin. Unfortunately at the present time insulin cannot be taken by mouth without losing its effectiveness. It has to be given therefore by daily injection, which is what makes so many persons dread this form of treatment. If you have been started on insulin, either your doctor or a nurse will instruct you in the proper techniques for using this method. You must make sure you understand thoroughly. You must also make sure you follow the method wisely. A serious overdose of insulin can kill in a few minutes.
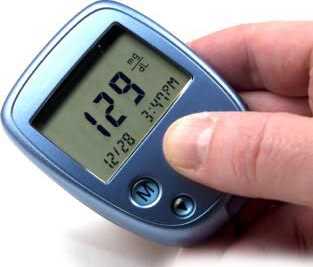
How can I tell when my diabetes is controlled?
In the past the only way to easily do this was to test a sample of urine. This however is not very accurate, though it can give a very rough guide. For many years now instruments called glucometers have revolutionised the effectiveness of treating diabetes. These allow the blood itself to be measured at any time, providing an accurate reading in a minute or two. These measurements can be done by the patient at any time, in any place, as often as necessary. This means that you, the patient, can effectively and with a good deal of precision, treat your own condition. This is invaluable in maintaining your blood sugar in the normal range. All diabetics should acquire a glucometer and become skilled in its use.
Your doctor will see you from time to time, and will usually want to see the record of the glucometer readings that you have taken. These should always be stored in a diary for instant review.
I know that I can't eat any sugar. What other food items should I avoid when I have diabetes?
It is a common and unfortunate myth that diabetics have to avoid taking sugar. Many persons suffer unnecessary discomfort because of the absence of sugar in beverages and food. The reason for this may be the feeling that since a diabetic already has "too much sugar in the blood" that any more sugar is bad for him or her. The truth is happily a bit more complex.
All carbohydrate foods (bread, ground provisions, pasta, sugar, etc) are digested in the body to produce glucose (the sugar the body uses for energy). So it doesn't really matter whether a food item is sweet (like sugar, which is also a carbohydrate), or not (like flour). They all produce the same glucose in the body. The important thing for the diabetic person is not to exceed the total amount of calories agreed on from day to day. As far as the body is concerned it really does not matter significantly how and where the calories originate.
The result of this truth is that there are no special food items diabetics have to avoid. What is required is simply to adopt sensible and practical eating patterns, and to adhere to one's daily calorie intake. It is because many sweet items (chocolates, cake, ice-cream, etc) contain so many calories that it is unwise to eat large amounts of these - this would result in an intake of carbohydrate much higher than required for the diabetic. It is also not generally known that fats contain twice the calories of carbohydrates - so avoiding, or cutting down on fatty meals would also be a healthy thing to do.
At the same time, diabetics need the same daily quota of food items that non-diabetics need. This means that you do need to get adequate supplies of vitamins, minerals, protein and yes, carbohydrate on a daily basis. Avoid bizarre and extreme food fads. Many of these have become popular of late, with many books being published touting their value. It would be a good idea to check with your doctor or dietician before embarking on any special diet you may want to start.
What ill effects does diabetes have?
Diabetes affects the entire body. It is still not completely clear why persons become diabetic, and some authorities are now beginning to think that diabetes, hypertension and obesity are all part of some obscure underlying disease process.
The main target of diabetes, especially if sugar levels are not well controlled are the small blood vessels of the body. As you may be aware, every single cell in the body depends for its nutrition on an adequate blood supply. This means that anything affecting the health of blood vessels has the ability to affect every cell in the body. Diabetes in some strange way, results in narrowing of the small blood vessels. This process can lead eventually to complete blockage of the vessel, thus completely starving the dependent tissues of blood. Some organs are more susceptible than others.
The main organs that suffer in long-standing diabetes are:
- The limbs, especially the feet
- The kidneys
- The eyes
- The heart
- The brain
- The erectile mechanism of the penis
- The nerves
Because of this the main problems that diabetes can lead to are fairly easy to identify.
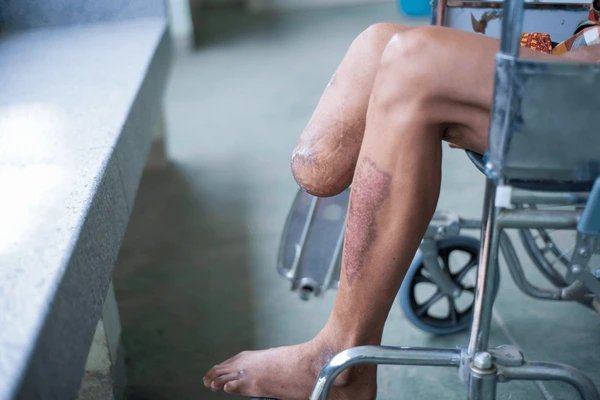

Amputations are an unfortunate late complication in many diabetics. Sores on the toes and feet often start from very slight trauma. These then become infected and because of the poor blood supply fail to heal. This then leads to gradually spiraling series of events which may end in loss of toes, or part of the limb. It is for this reason that you should NEVER attempt to treat yourself any wound, cut, abrasion or blister, no matter how insignificant it may appear at first sight. As long as you have diabetes, the wisest course is to see your doctor or seek attention at the clinic as soon as possible. This especially applies to nail punctures ("nail juks"), which will often require surgery to remove bacteria and dead tissue.
Kidney failure, though happily much less common, is nevertheless a dreaded outcome of diabetes, and underscores the need to maintain good control. Total kidney failure is fatal unless treated by dialysis. Usually though, failure is relative, making the kidneys less competent, but still able to maintain life.
Blindness is the end result of vascular failure in the retina, and may be compounded by cataracts, a clouding of the lens which can be accelerated by uncontrolled diabetes.
Heart attacks and strokes all result from blockage or narrowing of the arteries supplying these important organs. Strict control of diabetes will minimise the progression of the blood vessel changes that lead to these very major complications.
It is a little known fact that many men with diabetes, especially if associated with hypertension, may suffer from erectile failure as a long term result of diabetes. Erectile failure refers to the inability to initiate or sustain an erection of the penis. This is also due blood supply problems of the erectile mechanism in the penis.
Various kinds of nerve failure occur as well in long-standing diabetics. The most common is seen in the feet where many diabetics lose sensation - often without their awareness. Ulcers, sores and other problems often occur, because the feet lack the sensation of pain. Persons are simply not aware of trauma to the feet. This nerve failure can also affect the performance of the bladder and bowel leading to difficulty with urination and constipation.
There are many other problems associated with diabetes. In the female, pregnancy always makes diabetes more difficult to control, while at the same time, diabetes makes the pregnancy more complicated, and may lead to problems with the growth of the baby.
Can I pass my diabetes on to my children?
Not directly, nor did you inherit yours directly from your parents either. However it is very true that there is a strong genetic factor in the epidemiology of diabetes. One can become diabetic even when neither father nor mother has diabetes. However if one or both parents are diabetic, the chances increase significantly, especially if obesity enters the picture as well.
While you cannot do anything about your genes, you certainly can and should try to sensibly manage the things that are under your control - your diet, weight and exercise.

All this makes me scared. Is diabetes really so terrible?
The truth is it can be. The good news though is that as long as you recognize how serious diabetes can be, this can motivate you to do your very best to ensure your control never slips. Once you manage your diabetes sensibly, you can live a normal life span, all other things being equal. Sadly many diabetics become careless and in fact do stupid things - things they very well know they ought not to do. While this may be human, it is the main reason for the terrible tragedies some persons with diabetes suffer. Good consistent management is the way to optimum health with diabetes. The rules of diabetic management can be summed up in a few principles you should always follow:
- Commit yourself to a sensible diet, and don't stray
- Get regular exercise, and enjoy it
- Maintain your weight at the correct level for your height
- Follow your doctor's medication routine, if there is one
- Don't follow harmful diets or folkloric eating fads
- Check with your physician as per agreement
- Don't "run out" of your medication
- Maintain a positive, happy disposition
- Try to laugh, be happy and enjoy life.
Will my diabetes ever be cured?
Unfortunately there is no cure for diabetes at the moment. It is a chronic disease; this means that once you have diabetes it will remain with you for the rest of your life.
There are a few exceptions to this. Often diabetes develops in a pregnant person but clears up when the baby is born. Many of these women do however go on to develop full blown diabetes later in life. Sometimes taking certain drugs may cause diabetes, or a diabetic-like response, which will settle once the offending drug is withdrawn.
With these very few exceptions, most diabetics should clearly understand that this disease will be around for life. Learning to cope with it, and understanding it fully, will help you to enjoy life without too much hassle and heartache.
For the future, there are many research projects looking at ways to make diabetes more easily managed. Some of these are even looking for ways to achieve a cure. But this is way in the future.
Back

What is hypertension?
(Take note that this is a long article)
Every part of your body is dependent on a good blood supply for continued health. This blood is supplied by the pumping action of the heart, which forces blood through an elaborate system of vessels which reach all parts of the body. The pressure with which the heart drives this blood around the body is the blood pressure.
A typical normal pressure is 120/70 mm Hg (millimetres of mercury). As you can see there are two components to it:
Systolic pressure - the higher figure (120)
Diastolic pressure - the lower figure (70)
What this means is that when the heart beats, the force would raise a column of mercury 120 mm high; when it relaxes, the column of mercury would fall to 70 mm. This represents a considerable amount of work. But the healthy heart is very capable of doing this constantly, minute after minute, day after day, month after month, year after year without a moment's rest.
Hypertension of some degree is considered to exist when the blood pressure exceeds 140/90 mm Hg. This is a bit of an arbitrary figure, and largely depends on age. Generally it is acceptable for the blood pressure to increase slightly with age, so that a ninety year old person with a blood pressure of say, 160/90 would not be considered unhealthy. On the other hand, if a blood pressure of 140/90 occurred in a six year old child, this would be a cause for significant alarm.

How did I get hypertension?
Hypertension is a common condition the world over. However it is especially common among blacks, notably in the Caribbean and the USA. Apart from this racial link, it is also well known that hypertension, like diabetes, has strong genetic roots as well. If one of your parents has hypertension, your chances of becoming hypertensive increase; if both parents are affected, your chances increase even further.
There are also behavioural and dietary factors that play a part. Obesity, smoking, heavy and chronic intake of salt all increase the likelihood of your becoming hypertensive. The usual kind of hypertension is called essential hypertension. However in some cases, hypertension is secondary to some other disease or disorder. Kidney disease, thyroid disorders and some blood conditions, to name a few, may be responsible for hypertension. In such cases, treatment of the underlying condition often results in spontaneous correction of the elevated blood pressure. Some drugs are also associated with high blood pressure. Even supplements used by body builders may contribute to high blood pressure.
Finally stress and anxiety are well known to play a modulating role, and can add a few points to an already high blood pressure. Interestingly, there is a condition referred to as white coat hypertension. This occurs when a person is unusually anxious when attending a doctor's office. During such visits the pressure of such persons can rise dramatically, only to return to normal the minute they leave the office. These persons don't really have hypertension - they are only made to appear so by extreme anxiety when they come into contact with the doctor. Hence the term white coat hypertension - even though not all doctors today wear white coats!!
Why is hypertension so dangerous?
Untreated hypertension can be dangerous, even deadly. When the condition is untreated and severe, the heart, blood vessels and many organs in the body are made to operate with levels of pressure far outside the norm. The reaction of blood vessels to this high pressure is to constrict, or close down in an attempt to limit the high pressure. Over time this can lead to permanent narrowing of these vessels. This results in a lessening of blood flow through the organ. This lessening can progress to a complete block, resulting in immediate tissue death. How this tissue death manifests itself depends on where and what the organ is.
If this process occurs in the brain, the result is a stroke. Strokes may be fatal the first time, or leave the individual paralysed for life. Even relatively mild hypertension can contribute to stroke.
In the heart, this process leads to death of a part of the heart muscle, and is called a heart attack. Again, a heart attack can be massively fatal the first time. Happily many persons survive the first stroke and heart attack, but many also do not.
In Barbados, many individuals with long standing hypertension lose limbs, mainly the feet and legs as a result of poor circulation resulting from hypertension, either alone or in combination with diabetes.
The heart itself can suffer directly from having to work so hard continuously, and become so weak and inefficent at pumping that the person goes into heart failure. Such persons if not treated retain water and become bloated, have great difficulty breathing and may become extremely tired after walking a few steps.
There are many other ailments that hypertension contributes to in some way. Erectile failure in men (inability to get or maintain an erection), bad abdominal pains after eating meals, poor vision leading to blindness are only a few. Tragically, diabetes often co-exists with hypertension, making all these conditions that much worse.
Can hypertension be cured?
Hypertension that is secondary to other conditions may cease on its own when the main condition is corrected. Essential hypertension, on the other hand, cannot be cured at this time and remains for life. This is why it is so important for you to follow the entire therapeutic regime decided on between you and your doctor, without fail.
If there is no cure, how will I be treated?
There are two basic approaches to the treatment of hypertension. These two approaches are not exclusive of each other and in many cases are used together. The first is lifestyle changes. This has to do with weight control, diet and exercise.
DIET is important simply because many hypertensives are overweight. Despite what many persons think, being overweight has one and only one simple cause - overeating. Overeating is related to the energy needs of your body, which in turn are related to your energy output. A simple equation will make this clear:
Food intake = Energy output +/- stored fat
This simply indicates that the caloric value of the food you eat has only two fates in the body -
1. produce energy for work, exercise etc
2. any excess energy is stored as fat; on the other hand if there is not enough energy to satisfy your energy demands, fat is broken down to produce energy.
The aim of dieting is to supply the body with somewhat LESS energy than is required. This then forces the body to break down fat (stored energy from the past) to supply the extra energy. The result of this is that you lose weight. Weight loss by itself can have a dramatic and beneficial effect on the management of hypertension.
Hypertensives are also cautioned to reduce their salt intake. This can take some getting used to, but is easily achieved by not adding extra salt to food at the table.

EXERCISE is the other very important change many hypertensives can make to assist in the management of their condition. You should first check with your doctor to verify that you are in a fit condition for exercise. However with few exceptions almost everybody can walk; if you are otherwise healthy, especially if your hypertension is mild, then swimming, jogging and gentle sports can markedly improve your health. A look at the equation above shows that the effect of exercise is to make less food energy available for conversion into fat. Alternatively, exercise can accelerate the rate at which stored fat is broken down to produce energy.
When exercise and diet control are combined, one can derive the maximum benefit. Often in mild to moderate hypertension, this combination may be THE ONLY TREATMENT needed. It has been found that high blood pressure begins to respond to exercise even before weight begins to decrease. But exercise has to be meaningful. If you plan to walk, then you should do this at least 5 days per week, for an hour each time, and briskly. Many persons saunter casually for about ten minutes, every other week or so. While this may improve your mood, it is very unlikely to move a single ounce from your weight. On the other hand, it is quite okay to break up your exercise time in segments if you have to. For example, if you cannot spare a whole hour in the mornings, doing 30 minutes twice daily will produce the same effect as an hour at once.
If you are fit, more vigorous exercise can be undertaken, such as jogging, tennis, squash, cycling, etc. However it would be safe to check with your doctor first to make sure that this is acceptable.
DRUGS
While diet and exercise play very important roles in the management of hypertension many hypertensives sooner or later will require drug treatment. There are many kinds of antihypertensive tablets, all of which reduce the level of blood pressure, but by differing modes of action.
If you are taking tablets for hypertension, it is important to understand a few facts:
- Always take your medication as prescribed by the doctor
- Do not forget to take your tablets
- Do not double up (take a double amount) if you happen to miss a day
- Don't take anyone else's tablets, even if you are sure they look like yours
- Don't run out of medication. Always restock when you have a week's medication left.
One very important caution is to avoid the well meant but often misguided advice of the many friends and acquaintances who will urge you to try this and that. All countries have their folklore regarding disease, and Barbados is no exception. However many of these nostrums and concoctions have absolutely no proven worth in combating hypertension.
One other very important bad practice it to shop around. This involves seeing many different doctors for the same condition, often without letting doctor B or C know about the medication prescribed by doctor A. Such persons often end up with bags of drugs, totally confused about what to take. Worse yet, they may end up taking drugs that should not be combined together.
I don't want to take drugs. I've heard they have harmful side effects; is this true?
A side effect is an action in the body that is not desired, and that may be unpleasant or harmful. It is true that most drugs have side effects of some kind. These side effects often are related to the quantity of drug taken - these are toxic effects. Other effects may not relate to the actual amount of drug, but to the drug itself - allergic reactions.
If the dosage of the drug you have been prescribed is appropriate, you should have minimal (if any) side effects, and none should be serious - unless you happen to be allergic to the medication. Trivial side effects may include upset stomach, vomiting, cough, constipation or diarrhoea, urinating frequently, dryness in the mouth, headache and dizziness.
As long as these are mild and transient you need have no fear. If however they are severe or constant, or if you develop skin rashes, swelling of the face, fever, fainting, inability to pass urine, a racing pulse or palpitations, marked sexual problems (in men), or any other distressing symptoms, then you shoud immediately stop the medication and call your doctor, taking the medication with you. If your own doctor cannot be reached, then you ought to see any other available physician immediately.
A well tolerated durg will do its job of reducing the blood pressure without any perceptible side effects. Since they scores of drugs available for the treatment of hypertension, with due patience a drug can be found that will work well for you.
What are the complications of hypertension?
Hypertension affects the entire body. Some authorities are now beginning to think that diabetes, hypertension and obesity are all part of some obscure underlying disease process.
The main target hypertension are the heart, and the small blood vessels of the body. As you may be aware, every single cell in the body depends for its nutrition on an adequate blood supply. This means that anything affecting the health of blood vessels has the ability to affect every cell in the body. Hypertension, like diabetes, results in narrowing of the small blood vessels. This process can lead eventually to complete blockage of the vessel, thus completely starving the dependent tissues of blood. Some organs are more susceptible than others.
The main organs that suffer in long-standing hypertension are:
- The limbs, especially the feet
- The kidneys
- The eyes
- The heart
- The brain
- The erectile mechanism of the penis
Because of this the main problems that hypertension can lead to are fairly easy to identify.
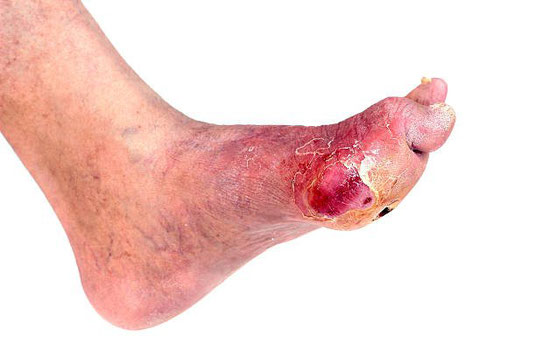
Amputations are an unfortunate late complication in many diabetics and hypertensives. Sores on the toes and feet often start from very slight trauma. These then become infected and because of the poor blood supply fail to heal. This then leads to gradually spiralling series of events which may end in loss of toes, or part of the limb. It is for this reason that you should be very cautious in attempting to treat yourself any wound, cut, abrasion or blister, no matter how insignificant it may appear at first sight. The wisest course is to see your doctor or seek attention at the clinic as soon as possible. This especially applies to nail punctures ("nail juks"), which will often require surgery to remove bacteria and dead tissue.
Kidney failure, though happily much less common, is nevertheless a dreaded outcome of hypertension and diabetes, and underscores the need to maintain good control. Total kidney failure is fatal unless treated by dialysis. Usually though, failure is relative, making the kidneys less competent, but still able to maintain life.
Blindness is the end result of vascular failure in the retina, and may be compounded by cataracts, a clouding of the lens which can be accelerated by diabetes.
Heart attacks and strokes all result from blockage or narrowing of the arteries supplying these important organs. Strict control of hypertension will minimise the progression of the blood vessel changes that lead to these very major complications.
It is a little known fact that many men with hypertension, especially if associated with diabetes, may suffer from erectile failure. Erectile failure refers to the inability to initiate or sustain an erection of the penis. This is also due blood supply problems of the erectile mechanism in the penis.
There are many other problems associated with hypertension. In the female, pregnancy always makes hypertension more difficult to control, while at the same time, hypertension makes the pregnancy more complicated, and may lead to problems with the growth of the placenta and baby.
This sounds terrible. Can I live a normal life with hypertension?
Fortunately, the answer is yes. Most hypertensives fall into the category of mild to moderate, where treatment is happily rather easy and routine, as long as commonsense prevails. The following tips should be observed:
- Commit yourself to a sensible diet, and don't stray
- Get regular exercise, and enjoy it
- Maintain your weight at the correct level for your height
- Don't smoke or drink
- Follow your doctor's medication routine, if there is one
- Don't follow harmful diets or folkloric eating fads
- Check with your physician as per agreement
- Don't "run out" of your medication
- Don't take extra salt in your diet
- Maintain a positive, happy disposition
- Try to laugh, be happy and enjoy life.

Can I pass hypertension to my children?
Not directly, but it is true that there is a strong genetic factor which operates in hypertension. If one parent is hypertensive, a child will have an increased tendency to develop the condition later in life, as opposed to a child with normal parents. If both parents are hypertensive, the risk increases.
What parents often pass on to children, apart from genes, are bad lifestyle practices - such as distaste for exercise, lazy habits (like long hours watching TV), bad eating choices, acceptance of obesity as being "no big thing" etc. You cannot help passing on your genes, even if they are not the best, but you certainly can teach your children, by your own example, how to live a healthy lifestyle.
I have heard that as long as my head doesn't hurt that my pressure is alright; is this true?
This is NOT true. Many persons have this totally false belief that high pressure usually causes headache. This is false. The majoirty of persons with hypertension are totally unaware of their condition unless the pressure is measured with a blood pressure machine. What is true is that dangerously high blood pressure can cause headache. When this happens unfortunately, such persons are in severe and often imminent danger of a major complication - such as stroke.

Obesity is now almost a worldwide epidemic, affecting millions of adults and children. The reason for the seriousness with which it is now being met has to do, not so much with it's cosmetic challenges - which are considerable - but with the significant health deficits attached to being obese.
These result in millions of dollars having to be spent worldwide in treating the long list of other diseases that obesity brings in its wake. These include
- diabetes
- hypertension
- heart disease, including heart attacks
- some forms of cancer
- stroke
- gallstones and gallbladder disease
- limb amputations
- deep vein thrombosis (blood clots)
- peripheral vascular disease (poor blood supply to the feet)leg and foot
- ulcers
- poor fertility in females associated with difficulty getting pregnant
- eye diseases like cataract and blindness (mainly resulting from accompanying diabetes and/or hypertension)
- early arthritis (caused by the excessive weight borne by various joints)
- breathing difficulties like sleep apnea
- and generally poor health leading to shorter life span overall
Added to this impressive (but incomplete) list are a plethora of psychological issues related to being fat, especially in young boys and girls during their years at school who may be teased about their weight. This may also be followed in early adulthood by difficulty finding a love mate. More trivial difficulties have to do with wardrobe issues like finding appropriate clothing for the seriously overweight. Society generally does not like obese people.
So, what is the cause of obesity?
At the most basic level, obesity results from a mismatch between food eaten and energy expended and can be represented by a simple equation:
Food eaten = energy expended + fat stored.
What this equation says is that there are two and only two dispostions for the food you eat on a daily basis. It is used to supply the energy needed for daily living. This includes your basal metabolism such as maintaining your body temperature, brain activity, keeping your heart beating, muscles working, etc. Since the body does not waste energy, if there is any "energy" left over after these activities, it is stored as fat.
You can therefore see how obesity occurs. If you consistently eat more food than is needed for your daily metabolism, you will store the extra as fat. Over time this will lead to a significant deposit of fat, and you become obese.
But look at the equation again. Notice that the relationship between energy expended and fat stored is a two way process. This is the good news and explains how obesity can be treated. If the food eaten is less than that required for the body's daily activities, the process is reversed and fat is broken down to supply energy. The result is that you lose weight.
To get a better understanding of obesity, you need to understand the chemistry of foods. While there is a dizzying variety of food items in the world, there are only 5 basic food categories -
- carbohydrates
- fats
- proteins
- minerals
- vitamins
There are other items in foods that are required for health that don't fit into any of these categories like fibre, but for this discussion these can be ignored.
Carbohydrates form the staple diets the world over and include well known items like flour, maize, roots (potato, cassava), rice, etc. Carbohydrates, irrespective of source, are all broken down in the body to glucose and utilized for energy production or fat storage. All carbohydrates produce 4 Calories of energy per gram. Sugar is also a carbohydrate and like all carbohydrates will produce 4 Calories of energy. The fact that sugar is sweet is completely irrelevant to its energy content. It is therefore not worse (nor better) in the context of obesity than any other carbohydrate. Ethanol - alcohol - is also an energy source, but contains about 6.5 Calories per gram - more than other carbohydrates.

Fats and oils (oils are just liquid fats) are an essential food item which we all need. Unlike carbohydrate however, a gram of fat or oil contains twice the energy content of carbohydrate - nearly 9 Calories. Examples of fats in our diet include animal fat, butter, cooking oil etc. Apart from supplying energy, fats contain essential ingredients that the body needs for health.
Proteins are derived mainly from meat and fish, and are broken down in the body to amino-acids from which the body then assembles it's own proteins. Like carbohydrates, proteins contain approximately 4 Calories per gram but it is important to understand that proteins are generally NOT used for energy. Proteins are used as a building material in the body, mainly in its muscles and other soft tissues like brain, blood and so on. During times of severe starvation protein is metabolized for energy, but this is at the expense of important structures like muscles, brain, liver etc. Prolonged starvation leads to death precisely because of this wastage of important organs.
Vitamins and minerals, including water and salt are vital for health, but contain no calories whatsoever. You therefore CANNOT become obese from drinking water or eating salt items (though this, in excess, will cause other problems).
Let's get back to obesity. Say your job is mainly sitting at a desk all day. Let's also assume you don't do any significant exercise (walking, jogging, swimming, cycling). Most studies indicate that you will need in the region of 1800 to 2000 Calories daily. The actual amount will depend on your body size and age to a lesser extent. Assuming you're an adult and are no longer growing physically, if you consume on average 1800 to 2000 Calories a day, you will NOT gain any weight, since you are expending exactly what you are consuming. If on the other hand, your diet contributes 2500 Calories daily, you will store 500 Calories a day. A pound of body fat contains about 3500 Calories, so your weight will increase by about 1 pound a week. In a month, you will gain 4 pounds. In six months, nearly 25 pounds. At this rate, you will gain nearly 50 pounds in a year of over-eating. (These figures are an approximation. As your weight increases, your energy requirement will increase as well, since just walking means you need more energy to move a bigger mass etc, but you get the point).
Consider another scenario. Your job still entails desk work, but now you jog for an hour on mornings. Jogging for an hour will burn about 500 Calories. You still eat 2500 Calories a day, but you will not gain any weight. Your diet is fully consumed in your exercise and daily metabolism. This is the ideal place to be.
Consider one more scenario. Your job entails desk work and you jog for an hour every day. But now your diet contains only 2000 calories, while your activities consume 2500 Calories. This will force your body to find 500 Calories a day from somewhere to make up the deficit. The source will usually be your fat stores. The body will break down a few ounces of fat on a daily basis to supply the missing calories. The result? You will lose weight.
If you think this is simplistic, you're right. Energy logistics in the body is a complex interplay of genetic and biochemical factors that defy simple explanations. Nevertheless, the above scenarios represent a true picture of the science. Your body is ruled by laws that are very precise, if not precisely understood. It cannot flout the laws of biology. So people who weigh 300 pounds, yet insist they "don't eat much" are simply fooling themselves. You CANNOT put on weight as fat without consuming, or having consumed, excess food. What may be true is that an obese person, having put on a large amount of weight in the past, may now revert to consuming on a daily basis what they are expending in energy. They will not put on any MORE weight. However they will still have the legacy of past excesses in the form of extra fat.

So how does one lose weight?
It should be clear by now that there is only one basic way to lose weight. You need to consume fewer food Calories on an average daily basis than the body requires for it's daily activities. This can be achieved by a combination of events.
- Increase your energy output - ie exercise
- Reduce your energy intake - ie limit your food intake
- Do both.
It should be clear that doing both (increasing exercise and reducing food intake) would produce the best results. Let us now consider how many Calories are consumed in various exercises and contained in various food items.
Calories burned during physical activities will depend on many variables, like your weight and how vigrously and how long you perform the activity. The following are a rough indication assuming you perform the activity for one hour and weigh about 150 pounds. If you are heavier, you will burn more calories.
For more information see the following sites:
www.health.harvard.edu/diet-and-weight-loss/calories-burned-in-30-minutes-of-leisure-and-routine-activities
http://calorielab.com/burned
The following tables list common exercises and calories burned.
| Exercise activities | Calories burned |
| Bicycle riding, leisurely | 200 |
| Bicycle riding, moderate | 500 |
| Bicycle riding, fast | 1000 |
| Walk / jog | 340 |
| Jogging, general | 400 |
| Running at 6 mph | 600 |
| Running at 10 mph | 1000 |
| Running up stairs (1 hour) | 900 |
| Strolling slowly | 68 |
| Walking at 3 mph level | 156 |
| Walking uphill | 340 |
| Walking very fast | 374 |
| Dancing, ballroom | 258 |
| Quiet TV watching | 0 ** |
| Browsing the web | 0 ** |
| Sleeping | 0 ** |
| ** apart from basal metabolism |
The following table list common food items and calories contained.
| Food Items | Calories contained |
|
Apple, medium |
72 |
|
Mango large |
200 |
|
Banana medium |
105 |
|
Beer, 12 ozs |
155 |
|
Bread, one slice |
66 |
|
Butter, salted, 1 tbsp |
102 |
|
Carrots (raw, 1 cup) |
52 |
|
Cheddar cheese (1 slice) |
113 |
|
Chicken breast (3 ounces) |
142 |
|
Chili with beans (1 cup) |
287 |
|
Chocolate chip cookie |
59 |
|
Coffee (regular, black) |
2 |
|
Cola (12 ounces) |
136 |
|
Corn (canned, 1 cup) |
180 |
|
Egg (large, scrambled) |
102 |
|
Granola bar |
193 |
|
Green beans (1 cup) |
40 |
|
Ground beef patty |
193 |
|
Hot dog (beef and pork) |
137 |
|
Ice cream (vanilla, 4 ounces) |
145 |
|
Jelly doughnut |
289 |
|
Ketchup (1 tablespoon) |
15 |
|
Milk (2 percent, 8 ounces) |
122 |
|
Mixed nuts (1 ounce) |
168 |
|
Oatmeal (plain, 1 cup) |
147 |
|
Orange juice (8 ounces) |
112 |
|
Peanut butter (2 tbsp) |
180 |
|
Pizza (pepperoni, one slice) |
298 |
|
Pork chop |
221 |
|
Potato, medium (baked) |
161 |
|
Potato chips (1 ounce) |
155 |
|
Raisins (1.5 ounces) |
130 |
|
Red wine (5 ounces) |
123 |
|
Rice (1 cup) |
205 |
|
Shrimp (3 ounces) |
84 |
|
Spaghetti (1 cup) |
221 |
|
Tuna (light,3 ounces) |
100 |
|
Yellow cake (one piece) |
243 |

If you carefully study this information, you will see why it is so easy to get fat. Suppose you ate, in one day,
- two slices of yellow cake (500 Calories),
- a couple of mangos (400 Cal),
- a slice of pizza (300 Cal)
- a nice thick cheese sandwich (300 Cal),
- washed down with a couple of beers (300 Cal)
you would already have consumed 1800 Cal, and you haven't yet eaten your main meal of the day, which might easily add another 500 Calories, for a total of 2300 Cal.
Now, to burn the same number of calories, you would have to:
- ride (leisurely) for half an entire day;
- or ride extremely fast for 2 hours;
- or jog for 5 hours;
- or dance for nearly 12 hours.
Habits that can make you obese
Quite apart from simply eating too much, there are a number of bad habits that contribute to obesity. Not surprisingly, snacking is probably number one. Nearly everybody is accustomed to snacking on something now and then between meals - the odd banana, orange, pack of nuts etc. This is usually quite harmless. However for some, snacking is a continuous process that never stops, day in, day out. Often the food items are high calorie items like chocolate, cake, sweat bread, sweet biscuits, sweet drinks, hot dogs and the like.
A related habit is eating in response to depression, unhappiness and anxiety. Worse is when snacking is coupled to inactivity like watching TV or browsing the web. Not only are you packing on calories but you're doing absolutely nothing physical. A recipe for disaster.
Remember also that alcohol contains roughly 6.7 Calories per gram, more than carbohydrates. So drinking alcohol while snacking compounds the problem.
The last habit that many obese people acquire is simply denying the problem. Some of the famous denial mechanisms are:
- "I have big bones"
- "I was a big baby"
- "I really don't eat much, swear to God"
- "It was the pregnancies that did this"
- "I drink a lot of ice water"
- "I have a hormone problem"
- "It's in my genes - my mother fat and my father fat"
- and lots more.
How do I lose weight if I am already too fat?
The first thing is TO AVOID CRASH DIETS AND FOOD FADS.
Crash diets may work but are bad for two very good reasons. The first is that they are by nature unsustainable; they are not designed to be continued for life. The second is that they can be quite harmful physiologically, because they are often unbalanced. A related reason is that they are often quite unpleasant as well.
Food fads are to be avoided for the same reasons - they are usually simply bad for you and just unscientific. "Back to Eden" type diets that say you cannot eat various foods before certain times of the day, or you can't mix food items at any one meal, etc, are, in a word, rubbish. Stay away from all of these.
Losing weight requires just two simple ingredients: common sense and endurance, the ability to stick to a safe, sensible program. The following is a guide to a safe, scientific, sustainable weight loss program.
Analyse your current (or past) diet to see where the problems are. You are either eating too much of everything, or you are consuming too many energy rich foods. Remember that eating too much of even "good" foods will make you put on weight. Are you eating too many meals? Are you eating too much at any one meal? Is your diet too rich in fatty, greasy, salty fast foods? Or too high in buttery sweet items like cake and chocolate? Whatever the abnormality, correct it. Aim for a healthy balanced diet, home cooked and high in fruits and vegetables. One main meal a day is all you need.
Exercise at least 5 days a week for an hour or more. If you are not fit at the moment, start gradually, say by walking for 30 minutes, increasing gradually until you hit your target. Remember that walking is not by itself very energetic. Add a jog for about 10 minutes if you can. Or start swimming. Or learn to dance. Some people hate the rigour of walking; so try a sport like tennis or volley ball, etc. Remember though that sporting activities make you dependent on having other people to play with. Walking, jogging, etc are activties that you can do completely alone.
Stick to it. Don't let silly excuses derail you. It may be raining, but your skin won't melt in the rain. If you let rain stop you from exercising, you'll be stuck for the entire rainy season - nearly 4 months of the year. Don't let people derail you - "Lord, chile, you looking so small. You sure you en sick?" Tell them to mind their own business - but do it kindly - they may mean well!

If you know you simply don't have the guts for it, then get a partner who can keep you at it. A husband (your own, that is!) or wife, or a good friend. If none of these work, then you might consider a good gym. Emphasis is on "good". Several gyms focus on "building muscle" and encourage clients to take various protein powders and other potentially dangerous food additives etc. Avoid these like the plague.
If you have any doubts about your heart and its ability to handle exercise, consult your doctor. You probably should in any case if you weigh more than 200 lbs, have not exercised for years, are diabetic or hypertensive, or experience undue fatigue or chest pain while exercising.
So, good luck to you. Remember, your body is really all that you have. Smart people look after themselves. Only a fool would ill-treat his/her own body. Obesity is a crime against your own body. Finally, if you do the right thing, your body will respond. YOU WILL LOSE WEIGHT.

Alcohol
(This is a long article)
Problems with alcohol can be looked at from two different perspectives -
- alcohol abuse, and
- alcohol dependency or addiction
Alcohol abuse occurs when the use of alcohol causes impairment in the person's life, work or ability to function normally in his or her environment. Alcohol addiction occurs when the person has a psychological need for alcohol and cannot do without it. It is therefore possible for some persons to occasionally abuse alcohol without being addicted. However nearly all addicts, by virtue of their chronic and irrestible craving for alcohol, will also be classified as abusers.
But I don't think I have a problem at all...
Few alcoholics are willing to admit to being an alcoholic, simply because of the bad connotations that this label implies. However, if drinking alcohol has caused impairment in :
- your family life
- your work
- your social responsibilities - OR
- you cannot function without drinking
THEN you have, quite frankly, an addiction to alcohol.

What causes alcoholism?
Problems with alcohol are more common than you think. Statistics in Barbados may not be easily available, but in the USA for example, 90% of the population drink (not abuse) alcohol. Of this number, about 40 - 50% of males have occasional alcohol induced problems (abuse), while only some 10% males and 5% females are chronic and persistent abusers or addicts.
Many factors are involved in producing alcoholism.
Society
Alcohol drinking exists in all societies the world over. In some, especially in the western world, its use is actively promoted by advertising, television, Hollywood, sporting concerns and the like.
Family practices
Many persons grow up seeing their parents, especially fathers, drinking in the home. It is therefore only natural for these persons to accept drinking as a normal activity.
Genetics
There is strong evidence that a genetic factor is involved in alcoholism. Large studies have indicated that relatives of alcoholics themselves have a greater chance - as much as a four fold increase - of becoming alcoholics. This tendency has been seen even in twins separated at birth and living apart from each other, without any knowledge of the other's lifestyle.
Peer pressure
Many persons first begin drinking in high school or university when pressure from peer groups is at its greatest. Some drink only experimentally and may not continue, but many more continue to drink.
Stress, frustration
Stress of some kind afflicts nearly everyone in society today. A poor attitude to problem solving, or difficulties handling stress can be the final straw in inducing alcoholism.

Is alcohol dangerous?
It certainly is - hence the recent very strong emphasis to turn people away from this potentially deadly drug. The World Healthy Organization (WHO) estimates that the health of the world would increase by an almost unimaginable degree if people the world over would do three simple things: -
- stop drinking
- stop smoking
- lose weight
The dangers of alcohol are many. It may surprise you to know that alcohol is often used in the laboratory to preserve tissue samples. It does this by rapidly killing living cells. It is therefore a tissue poison when used in massive excess.
Alcohol has many effects on the brain. Indeed this accounts for its popularity and widespread use. It is a sedative, and like all sedatives, depresses brain activity. However the sedative effect initially - and paradoxically - causes excitation.
This is very often seen at parties where people are drinking, and soon become merry - and often a little silly. The reason for this initial apparent stimulation is that alcohol at first depresses that part of the brain that is responsible for control, reserve and inhibition.
If drinking is continued, then the sedative effect soon becomes very obvious. Coordination is lost - hence the slurred speech and staggering walk; beyond this phase, sleep and sometimes frank coma, may occur if a considerable amount of alcohol has been taken.
Both in chronic drinkers, as well as in persons who only take alcohol occasionally, fits (epileptic attacks) may occur. Fitting occurs when a part of the brain begins to experience unusual electrical activity. Very occasionally these rum fits as they are called, may result in acute death. This may happen if the person gets involved in an accident (falls in the sea, crashes a vehicle, gets knocked down), or if he chokes or suffocates during the fit. This may happen because during a fit a person may vomit or the tongue may obstruct the airway.
Many alcoholics suffer some degree of memory loss, especially for events while they are drunk. This is even more tragic if some serious act is committed and not remembered. Many men while drunk may crash a car - even killing or maiming someone else - and not remember. Or may beat up their wives, and have absolutely no memory of this event on sobering up later. This memory loss may be due in part to vitamin B defiency (poor general nutrition), but also may be a component of severe brain disease called encephalopathy. Xrays of the brains of chronic alcoholics often show evidence of atrophy (decreased brain tissue), and some persons will go on to develop an irreversible dementia (senility).

Because of the severe destructive effects alcohol can have on the brain, some chronic alcoholics develop frank psychoses - they literally go mad, and may spend the rest of their unfortunate lives in a mental asylum.
Violence and alcohol very often go together. This is especially so in young males, where fighting under the influence of alcohol may lead to fatal injuries. As already pointed out, this violence may also manifest itself in abuse both of spouse and children in the home.
Effects on the rest of the body.
Alcohol can damage the esophagus (swallow-pipe) and stomach, causing acute inflammation of these organs. This results in upper abdominal pain, vomiting and anorexia. Sometimes the vomiting is severe enough to cause bleeding from the esophagus. If the inflammation in the stomach progresses, ulcers may develop. Even in a modern medical environment, an ulcer that bleeds massively, or perforates (eats through the wall of the stomach) can lead to death.
Just behind the stomach is an organ called the pancreas, one of the major digestive organs, and the only organ capable of making insulin (which prevents diabetes). Acute pancreatitis is well known to be caused very often by alcohol. This condition may be mild and self-limiting, but can cause death if severe. The reason for this lies in the powerful enzymes that the pancreas produces. These are capable of dissolving almost any food taken - its usual job. When the pancreas gets inflamed, these same powerful juices can go berserk and literally dissolve away both the organ itself, as well as the person.
The liver is the major factory of the body. Not only does it manufacture an astounding array of proteins and other chemicals needed for life, it is also mainly responsible for detoxification (getting rid of toxins). Life is not possible without a functioning liver. Unfortunately, as soon as alcohol is absorbed from the intestine, it goes directly to the liver (as do nearly all the foods one eats).
The liver then proceeds to metabolise the alcohol. However in so doing, a number of harmful chemicals are produced. The combined effect is that over time, the liver cells become damaged. Valiantly the liver attempts to repair the damaged areas, and for years manages to keep functioning. However eventually cirrhosis develops. Even at this stage the person may not be aware, because of the tremendous capacity of the liver. However when approximately 75% of this massive organ becomes impaired, symptoms then develop - of two major kinds.
The first kind has to do with the inability of the liver to perform its wide range of functions normally. This leads to:
- swelling of the liver itself
- accumulation of large amounts of fluid in the abdomen (ascites)
- difficulty in the ability of the blood to clot normally
- failure to produce enough glucose for energy
- jaundice (yellow eyes)
- fatty deposits in the liver itself
All these maladies lead to lethargy and fatigue in the individual. If drinking is continued at this stage, death often results in less than 2 years.
The other effect of cirrhosis is to choke the vessels that normally carry the large amount of blood flowing through the liver. The blood then tries to find other pathways back to the heart. This leads to huge veins dilating in areas that were not intended for such large blood flow. One group of such veins is in the lower esophagus. These unfortunately are very fragile, and not uncommonly will rupture suddenly. Tragically this can result in massive bleeding and acute death.
Persons with cirrhosis are also at increased risk for developing cancer of the liver, usually after a number of years.
Alcohol can also affect the inside of the bones where marrow is found and where red blood cells are produced. This leads to anemia. Cells of the immune system are also depressed by alcoholism, rendering the affected individual more prone to develop acute and chronic infections.
Like the liver, there is only one heart. This organ suffers eventually from the effects of chronic alcoholism as well, developing what is called a cardiomyopathy which may lead to heart failure. Heavy drinking also leads to increase in the blood pressure, and may also cause irregular beating of the heart.
While alcohol is often said to stimulate the individual sexually, paradoxically it also decreases the ability to have and maintain a good erection - a truly unfortunate combination of heightened desire and lowered ability!
If alcohol is taken in pregnancy, it can have severe effects on the developing baby. Alcohol crosses the placental barrier from mother's blood to baby's blood.
This can cause major disturbances in the organs of the growing child, leading to malformations of teeth, face, eyes, the hearing mechanism, heart and brain.
Perhaps the most unfortunate effect alcoholism has on the addict is loss of personality; self-esteem goes, work may eventually go when the person becomes incapable of productive activity, family may go when spouse and children become fed up with abuse, or simply lose patience; health invariably goes; friends gradually disappear (even drinking partners); the only companion then left is the bottle.
At this stage the alcoholic is one step away from death - usually from the bottle. Before this stage, there are usually several failed attempts to stop drinking. These usually occur after some frightening event like a fit; but after a drink-free period of weeks or months the drinking starts again, tentatively at first, then with increasing abandon.
What's the point then? - it seems that I am lost.

That really all depends on YOU. The simple reality is that the only person who can effectively change your life is YOU. That you have not yet achieved this (presumably) may be due to some simple facts that need to be examined.
You cannot change until you have accepted the truth of your condition
Once you have made this first step, the whole world (except your drinking partners) stand ready to help you.
There are a few logical steps you can take to quit the alcohol habit.
Once you make a definite decision to stop drinking, you will succeed.
The truth.
Even if it hurts to accept your condition, you must face up to it. Admitting that you have a problem with alcohol may be humiliating at first, but it gives you the necessary amunition to start on the road to recovery.
You have help.
True friends, family, your doctor(s), the Church (whatever your flavour), both secular and Christian counselors, the internet, Alcoholics Anonymous, God himself and various other support groups - all will fall over you to help, once you make the all-important decision to quit drinking. All these entities (and more) will do all that is humanly possible to assist you. Indeed, children, wives and husbands are often overcome with joy at such a decision. But take note: you will not get any help from your usual drinking buddies.
A firm decision
This is important. Even though you may slip, it is important to truly make a decision and stick to it. This is why it is so important to completely forget old drinking buddies, whose influence and companionship will do nothing to assist in maintaining the strength of your decision. Indeed, returning to the habit is often the result of a night out with the boys.
Logical steps
While emotions are important, they cannot take the place of hard thinking. Fear, anxiety, shame or some other emotion may have propelled you to consider quitting alcohol. However the only power that will keep you on the right track is a DECISION made with your brain. Do this - your emotions will follow in time. Then plan your strategy logically, and follow it. Remember, you are in a battle with an enemy that has killed many millions before you.
Okay, so what do I do to stop?
There are many parts to this, and the following is just one of many different strategies possible. I would suggest the following (not necessarily in this order, but all must be done).
- Get up right now (if you are at home) and immediately dump, throw away, get rid off, all alcohol in your house. This includes beer, wine, shandy and all other spirits or liquers.
- While you're at it, throw out the rum and raising ice cream - you really don't need the taste of alcohol any more.
- Call your wife, husband, children, pastor, doctor (etc) and tell them your decision.
- Make an appointment to see your doctor who will need to examine you and perhaps do some investigations, in preparation for your possible withdrawal symptoms (more about these in a moment).
- As soon as you have the physical support of your spouse, or a good friend, call your old drinking buddies and also inform them that you have decided to stop drinking. Don't discuss the matter, just tell them.
- Cancel your membership in any clubs, groups, or organizations where drinking is a normal part of the program. They can do without you for the time being, and so can you.
- Sign up with Alcoholics Anonymous, or some similar association dedicated to helping persons like yourself.
- If you are so inclined ( and it can help tremendously), find a religious organization, where fellowship, friendship, prayer and religious activities can give you support and encouragement.
- Take a deep breath - your journey back to health may be a rough ride.
Okay so far. Now what next?
Whatever happens, you will not drink alcohol. You must promise yourself this and stick to it. Most persons find the first two weeks or so the worse. A number of really hard and chronic drinkers will develop delirium tremens (the shakes). This is more than just shaking. It is a physical response from a body that has become dependent on the presence of alcohol for normal function. When alcohol is withdrawn, a number of neurological and biochemical events are triggered which result in violent shaking, sweating, an awful craving for a drink, hallucinations, anger, restlessness and insomnia. Such persons often have awful visual hallucinations where little green men may attack them, or they may hear voices etc. In such severe cases, hospitalization may be required for a few days. Most persons, thankfully, will not suffer so badly, but all will experience some degree of discomfort, restlessness and difficulty in this period. Whatever happens, you must resist the urge to drink.

In time, all these distressing symptoms will fade away, and you will find life taking on a new meaning. But be warned - your troubles are not over. The most dangerous period is perhaps not even the stage of the shakes. It is usually weeks or months afterwards, when you are well on the way to recovery.
You now feel secure. You are now in control of the situation. You no longer have that aching craving for a drink. You can handle it. So - you reason - what's the harm in a little sip now and then. Just one sip, mind you. Its not like you're going to have the whole bottle. Just one teeny sip.
Just one sip - and you're lost AGAIN. But not immediately. Nor the next day. Not even the next week. But that sip is FATAL. This is the most dangerous phase in staying dry. And the hard truth is - this phase can last for the rest of your life. Every day of your life, you must continue to resist that fatal urge for just one sip.
But I hear doctors saying now that alcohol is good for your heart. Is this true?
This is a two edged sword. Former studies were reported to show that persons who drank moderately (one to two drinks a day) tended to have less heart disease than persons who either didn't drink at all, or drank too much, but recent research has thrown serious doubt on the validity of these conclusions.
Another study followed two groups of young males from about age 20 to middle life; one group drank moderately while the other did not drink at all. After studying the outcome of these two groups, the conclusion was that one COULD NOT advise nondrinkers to start drinking alcohol. Quite apart from any beneficial effects moderate drinking may have on the heart, this study highlighted that overall, healthy nondrinkers were far better off in the long run, than moderate drinkers.
Now that I have stopped drinking, will my health return to normal?
You will certainly be healthier. Whether you will return to normal health will depend on the amount and type of damage alcohol has already done. Your general nutrition will clearly improve, since you will be eating better. No further damage will occur to your liver, but the degree of actual damage will really determine what further symptoms you will suffer. In many persons liver function improves dramatically after alcohol is no longer a part of one's diet. You can also expect your memory to improve with good food, and your general strength to increase with exercise and adequate sleep. Your doctor is the best person to advise you in this area.

Exercise
(This is a long article)
If there is one thing in the world that we all talk about but do the least about, it is exercise. Virtually from birth, we are told how great exercise is, and the tremendous benefits it can bring:
- It improves strength and endurance
- It strengthens the heart, muscles and bones
- It improves the mind
- It may delay the onset of various dementias
- It just makes you feel better
- It helps with bowel regularity
- It can improve sleep in people with insomnia
- It reduces blood pressure
- It helps regulate blood sugar
- It is a great all-round tonic
- It is completely FREE
- It helps you age better
- It can improve period difficulties in some women
- It improves the immune system
- It improves the mood
What is the best exercise?
There is no "best" exercise. Anything that gets you moving your muscles, deepening your breathing, stressing your bones and sweating a bit is good exercise. The "best" exercise for anyone depends on the goal of exercise.
If you are healthy, with no medical history, and want the highest level of fitness, you will most likely want to choose a vigorous and demanding exercise or group of exercises. Among the most demanding of exercises are:

- Running, jogging
- cycling
- fast swimming
- heavy gym workouts
- aggressive lawn tennis / squash
If you are middle-aged with hypertension and diabetes, you may not need or want the most vigorous kinds of exercise for obvious reasons. In such cases, the following might be better choices:
- Slower jogging
- Brisk walking, perhaps alternating with short jogs
- gentle swimming
- less aggressive lawn tennis
- free hand exercises
- dancing - ballroom, line
- skipping
Some people will add other disciplines like yoga and tai-chi. My personal opinion is that while these have their place, they are not "exercise", for the same reason that your daily normal routines (housework, taking out the garbage, reading the paper, washing the car, etc) also don't qualify. While all activity has merit, what sets exercise apart is that it should challenge your muscles and cardiovascular system and get you breathing more deeply than normal. It is also for this reason that simple walking on the flat, while good in itself, is seldom enough.
The problem today is that progress has robbed life of many of its "normal" physical challenges. Half a century ago, people did not need to "exercise". Exercise was built in to daily life. Few could afford cars, so people walked long distances or rode bicycles (ie exercised). They had no washing machines and had to hand wash or use the old Bajan jukking board (exercise). In the field, men cut canes manually and forked the land (serious exercise). Debushing was done, not with a weed whacker, but with a hoe.
Today, all that has changed. With cars, labour saving devices in the home and at work, few activities call for any effort. The hardest work many people do today is hit computer keyboards. The result is an epidemic of diabetes, hypertension and obesity. And the need to find other ways to exercise.
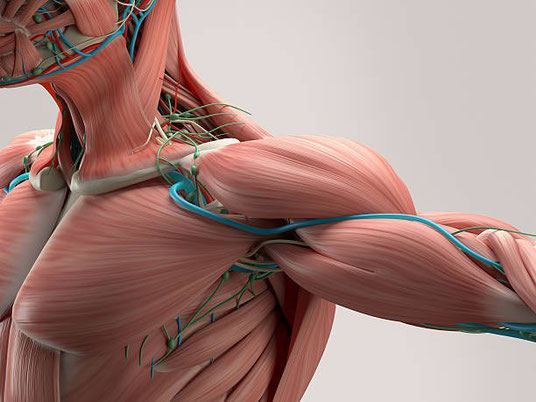
What does exercise really do?
The human body is a machine. Mechanical machines have motors, engines and various gears, levers or pulleys to do work. The human body (and other biological entities) have muscles, bones and tendons. Muscles provide the kinetic power to do work. A muscle element is a linear actuator (motor) made of two chemicals called actin and myosin that slide past each other when stimulated by a nerve. This leads to the muscle becoming shorter and pulling. Since muscles are connected to bones, when a muscle shortens, it pulls on the bones to which it is connected. Muscles can only pull.
If muscles can only pull, how can we jump or push or skip?
You might ask the same question of a car. Engines can only spin. So how does a car go forward or reverse? Motors similarly can only spin, so how do jackhammers drill into concrete? The answer with mechanics is various gears, pullers and levers. With biology the answer is joints, tendons and synergy with opposing muscle groups. When you use your hand to pull something, your biceps are contracting. When you push something away, your triceps (an opposing muscle) contracts while the biceps relaxes.
The benefit of exercise is that when a muscle works harder, it gets physically bigger and stronger. But that's not all. Behind all biological activity is a host of chemical reactions. With exercise, these reactions become more efficient. One aspect of this increased efficiency is the supply of glucose to the working muscle and the removal of waste products. This is done by the blood supply to the muscle. For this to improve, the heart has to work harder. The heart itself is a muscle that gets stronger with exercise, so a nice cycle begins as you exercise. Muscles begin to get stronger and demand more. The heart responds by getting stronger and supplying blood at a faster rate, so muscles can do more.
An important by-product of exercise is the production of carbon dioxide from the burning of glucose (and fat). This is gotten rid of by the lungs during exhalation. With exercise, breathing also becomes more efficient in taking in oxygen and releasing carbon dioxide.
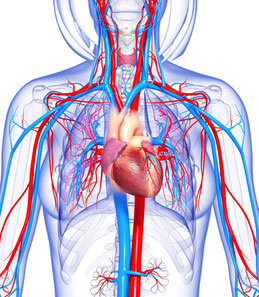
Of course, blood has to reach the working muscle. This is the job of your circulatory system, made up of arteries, veins, capillaries and lymphatics. All of these increase their efficiency as a result of exercise. Arteries remain supple and compliant longer and capillaries open up more easily to allow cells to respire. Without exercise, arteries more easily develop plaque which makes the walls hard and brittle.
Most people think of bones as....well, most people DON'T think of bones. But bones are alive and active instead of passive. Practice doing nothing and your bones gradually get thin and weak as they lose calcium. Calcium is the hard substance in limestone and other rocks. It's presence in bones determines how strong that bone is. With exercise, bones undergo two different kings of (good) stress.
As you walk or jog, the bones in your spine, pelvis and lower limbs are repeatedly undergoing compressive forces due to your weight and the pull of gravity. If bones were dead or passive, this would simply wear them down. But because bones are alive and active, they respond to this stress intelligently by asking the body for more calcium. They become stronger and denser. A stronger bone will fracture less easily than one that is thin and weak.
It should be clear by now why exercise is so beneficial. The entire body - muscles, heart, blood vessels, bones, and a whole range of chemical processes - all become more efficient. The result is vastly improved health, weight control and blood sugar management.
So why do so many people HATE exercise?
The short answer - when people are honest - is "laziness". They don't really hate exercise. It's just that early in the morning, the bed is nice and comfy and warm, so why leave it? Or it's going to rain. Or I'll start tomorrow. Or I'm too tired in the evenings. Or I'm just too busy with work. The great thing about exercise however is that once you start, you generally feel so much better. You're more energetic and tend to work better.
Is there such a thing as too much exercise?
Yes, there certainly is. As with anything, you can overdo exercise. You can push your body too hard, too fast, too far and for too long. This can result in muscle and tendon tears, stress fractures in bones, fatigue and joint injuries. Women who over-exercise often end up with period and menstrual irregularities. In really severe cases, acute heart failure may result.

A related situation is exercise in people with medical problems like previous heart attack, difficult hypertension, severe asthma, and the severely obese. During hard exercise it is common for the blood pressure to increase. In the healthy individual this is easily tolerated. A heart damaged by a previous heart attack or severe hypertension may not be able to support this. Similarly, a severely obese person who starts exercising too vigorously for the first time may end up in many different kinds of trouble - musculo-skeletal, cardiovascular and biochemical. In such cases, the wise thing is to check with your doctor first.
Other situations when exercise can be harmful include acute febrile illnesses like a flu, when recovering from major surgery, and when nursing an acutely swollen joint. In these and similar times, you need to rest and let healing occur first. The reason is simple: exercise is a form of stress and is normally good. But if the body is already under major stress (as in the conditions mentioned above), adding more stress can cause serious injury.
How often should I exercise?
In one word, every day. Many medical authorities will suggest two or three times a week is enough. If you are not trying to lose weight, are generally quite fit and healthy, this may indeed be enough to maintain your health. But such advice to me seems to suggest that exercise is some strange and wonderful activity. On the contrary, it should be a normal part of every day's routine, like bathing and brushing your teeth. Properly done, there is absolutely no reason not to exercise every day.
At what age should I stop exercising?
There is no age when you should stop exercising. Exercise will produce benefits at any age. What's important is to sensibly modify your exercise regime as you age so as not to injure yourself. Jogging 5 miles a day is completely acceptable at age 30. You wouldn't (probably couldn't!) do this at age 85, nor should you aim to. A brisk walk would be more sensible.

What about exercise during pregnancy?
Assuming you have no problems with the pregnancy, exercise is generally very safe in early and mid pregnancy, with due care to scale back the vigour and intensity of hard workouts. In late pregnancy, it would be best to be guided by your doctor.
What is the best time of the day to exercise?
It really doesn't matter when you exercise. Some people are morning movers. Some prefer evenings. Others do it at night. Just fit it into your schedule whenever it makes most sense to you. One advantage in morning exercise is that whatever challenges the days brings, it's already done. People who prefer evenings often find that unforeseen events can crowd exercise out.
The only caveat would be for those rare folks who like to exercise at midday, to make sure that the skin is protected from the sun's powerful rays. This is to avoid sunburn as well as more serious things like skin cancer.
I want to exercise but I have nobody to do it with.
Then do it alone. The bald truth is that when you get sick, you get sick alone. When you die, you die alone. There should be no problem getting healthy alone. But yes, many of us prefer company; the camaraderie of the group can help dispel the monotony of routine exercise. So find a friend, a buddy or a soul-mate. Or check out a gym. But if all fails, then do it alone. There's joy in talking to yourself while jogging along a quiet country road in the fresh breeze of an early morn.

Smoking
Historical sources date smoking as far back as 5000 BC, so it is clearly not a new activity. In its earliest forms smoking tended to be associated with various rituals, some social, some religious, some political and included cannabis and opium. This article concentrates on tobacco smoking.

The tobacco plant (genus Nicotiana) is native to the Americas and was smoked from earliest times by native American people. When the Europeans arrived in the Americas, they were instrumental in taking the plant and habit to the rest of the Western (and Eastern) world.
In the early days of tobacco use, it was actually thought to have beneficial effects on certain diseases like asthma, but gradually fears began to emerge among different people that smoking was generally harmful.
Many older celebrities and artistes adopted smoking for its style and glamour. People like Dean Martin and Nat "King" Cole smoked to encourage that huskiness of voice that was typical of those crooners.
But gradually patterns started emerging. Lung cancer was a rarity in the early 20th Century. But as smoking spread in popularity, it was observed to be increasing. What was also noticed was that it was significantly more common among men than women (men smoked much more than women). However up to about the 1960s it was mainly conjecture. It was around this time that a medical study was undertaken to investigate the effects of smoking. In time the evidence became overwhelmingly clear that there was a powerful link between smoking and lung cancer. You may recall that Nat Cole himself died of lung cancer.

Several major studies from all over the world have now proven the close link between tobacco smoking and :
- lung cancer
- stomach cancer
- oral cancer
- degenerative diseases of teeth and gums
- bladder cancer
- obstructive lung disease
- type 2 diabetes
- hypertension
- immune system depression
- nicotine addiction
- heart disease
- stroke
- foetal growth retardation
- vascular disease
The reason for this is the large number of dangerous elements (several thousand) contained in cigarette smoke, many of which are carcinogenic. Nicotine is a major ingredient and is responsible for the addiction that smoking can induce.
if smoking is so dangerous, why do so many people smoke?
In a word, marketing and promotion. Cigarette companies fought valiantly in the mid 20th Century to deny the harmful effects of their product. When that failed, they resorted to marketing. In 2019, tobacco companies spent a total of 8.2 billion US dollars on marketing and promotional activities - roughly 22 million dollars every single day. Much of this marketing is to young adults.
Hollywood smokes. A long list of very famous artistes, actors, actresses and various other performers have smoked on screen, and still do to this day. Smoking therefore has become synonymous with glamour, bravery, manliness and being cool and with it.

Impressionable young minds, mainly men but women too, then find this attractive, despite all the widely known ill-effects.
Indeed, next time you watch a movie, note carefully how the camera pans in to the actor as he lights up. All very deliberate and planned. What Hollywood never shows you is the same actors fighting addiction, lung cancer and finally death.
Peer pressure is a related factor. There is considerable pressure in a group to follow what the group does. People often start smoking to be accepted, to be fashionable, to be part of the crowd. However, when addiction sets in, they are hooked and it becomes a vicious cycle

Sports
Knowing how powerful sports and sporting events are, tobacco companies have for years sponsored sports, including baseball, tennis, field and track and football. In years past, several high profile sportsmen and women appeared in smoking adverts.
While this became unethical, the companies did not give up. Their billboards can still be seen at many sporting events year round, and now include many non-traditional sports like drag racing.
So smoking is here to stay. Some 480,000 Americans die every year from the effects of smoking. Worldwide, the figure is 8 million. Many more do not die, but suffer ill health, loss of productivity, decreased fertility and other less well documented negative effects of smoking. It does not have to be you.
How can I stop if I'm already addicted?
The first act is to recognize that if you continue smoking, you are driving nails in your own coffin. The second thing is to decouple your mind from all the influences that started you on your cigarette addiction - buddies, society, peer groups etc. The third is to be honest about your capacity to quit. The final factor is to be single-minded in your decision to stop.
If you honestly know that you can quit, just do. Stop. Don't slow down (half a pack for the first week, then two cigarettes a day, then none). Just stop and stay stopped. Understand that you will have a daily battle to resist the urge and fight the fight. Avoid all groups, parties and events where smoking is the norm. Make it easy on yourself and just don't go. If you continue to frequent such places, the urge will be even stronger, as well as the societal pressure.
If you know that you can't quit on your own, take advantage of the resources that are available to help you. Nicotine Anonymous may not be available in every country but has a web site here. You can also lean on wives, husbands, partners and non-smoking friends who have your interest at heart to assist. If you need professional support, there are psychologists and medical therapists who are available, as well as several online agencies.
How does addiction work?
Good question. Addiction covers many processes and states. Some may be mental/emotional/cultural and merely represent a strong habit. But true addiction goes way beyond this. It is present when the person's physiology actually needs the addicting substance to function normally. At this level, depriving the body of the substance leads to actual physical states where function is impaired. Nicotine addicts may shake and tremble during withdrawal. They may have difficulty sleeping, concentrating and eating and may be unable to work normally. Mood and temper may be unpredictable with large unexplained swings.
This is the same sort of behaviour seen in drug and alcohol addiction. It is caused by fundamental disturbances in brain chemistry and explains why addiction is so powerful and difficult to resist. It underscores the wisdom of avoiding all mind-altering agents in the first place, because when addiction sets in, you are no longer in control - the drug is.

The good news is that physiological dependence and the withdrawal period are time limited. They will come to an end IF YOU STOP AND REMAIN STOPPED. What happens in time is that the body's systems gradually return to normal.
Now some authorities will disagree with the notion of quitting completely. Others will suggest substituting less harmful and dangerous practices like vaping. There are also nicotine patches, as you probably know. My perspective - a personal one - is that all these simply kick the can down the road and may themselves (eg vaping) lead to their own problems. Why pussyfoot? Do it the hard way and get it over. But that's a personal view. You will need to make the decision that is right for you. Whatever you do, just get it done. You owe it to yourself.
Drugs and drug addiction
The human body is a chemical machine. It runs on biochemistry. Every cell contains a dizzying array of chemicals that take part in reactions which produce other chemicals. These control thinking, how and when muscles work, heart rate, vision, hearing, memory, mood, anger, joy. They control imagination, foresight and productivity. They also control religious ideation and its many counterparts.
The power of mind altering drugs - the subject of this article - is the capacity to do exactly that - alter the normally very precise chemistry of the brain.
Brain activity is driven by a number of chemicals called hormones. Those that we are familiar with (there may be many more yet undiscovered) are:
- serotonin
- dopamine
- oxytocin
- various endorphins
Hormones work generally by attaching themselves to various cells by means of chemical groups called receptors. When these receptors are triggered, cells respond in a number of ways, usually by producing, or increasing production of, various other substances including proteins. The affected cell may also respond by increasing its electrical activity. In the brain, a neural cell may synapse with (connect to) several hundred other neurons; this means that when one cell is activated, the process can spread in a logarithmic fashion to involve massive amounts of brain tissue.

What you may not know is that when you are happy, one set of hormones are bathing parts of your brain. When you are sad, another set of hormones are active. Same goes for anger, etc.
The clue to the power of drugs is that they can attach to the very same receptors that the brain's own hormones do. In other words, drugs can mimic the effects of the brain's own native chemicals.
It is no wonder then that a drug can make one happy, or sad, or angry. Another drug can make people feel close to God, or see devils coming at them. Another drug can induce (false) feelings of peace and quiet, or massive fear and anxiety.
Drugs can also cause hallucinations where people see little green men, hear voices telling them terrible things or make them paranoid and think people are attacking them. Drugs can completely alter normal behaviour. That is their power.

The list of agents that humanity has used and uses as drugs is long and goes back to antiquity. We are familiar with:
- alcohol
- cannabis
- hemp
- coca leaves
- cocaine
- tobacco (nicotine)
- heroin
- morphine
But there is a long list of more modern analogues and derivatives, many of which are times more powerful. These include:
- LSD (lysergic acid)
- amphetamine (speed)
- ecstasy - (3, 4-methylenedioxy-N-methamphetamin), or MDMA
- ketamine
- metamphetamine (crystal meth)
- PCP - angel dust
- mescaline
While many of these are illegal, several legal drugs are also implicated in drug addiction and abuse, like:
- sleeping agents like barbiturates
- pain killers like morphine, heroin
- depressants like valium
- fentanyl
Some other agents that have drug-like activity may come as a surprise, like:
- excessive use of coffee (caffeine)
- bath salts
- gasoline (sniffed)
- cough medicine

With all of these agents, the single issue is the effect on the brain to cause various states, most prominently:
- depression
- excitation
- pleasure
- hallucinations
- loss of inhibition
- reduction of anxiety
- addiction
In so doing, various receptors on neurons are activated and the brain responds in ways that are not consistent with actual reality. While happiness and peacefulness are great states, it is completely unrealistic to be in such states standing in the middle of the road with oncoming traffic. Under the influence of drugs, the brain will almost always make the wrong decision.
The addicted individual invariably loses contact with reality and engages in actions which are totally inappropriate and possibly dangerous. Hallucinations occur when people see or hear things that are not real. Their mother or wife may turn into an attacking lion and be killed in (false) self-defence.

Many youngsters brought before the court for various offences (burglary, assault, theft) admit to being under the influence of drugs.
There really is no place in a sane world for the scourge of drugs. But millions of people the world over are victims and it is this that fuels the manufacture and distribution of drugs. As you well know, it is a multi-billion dollar industry with famous cartels in Mexico, Colombia, Italy, the USA and many other countries like Aghanistan.
Battling addiction
This topic is familiar to hard illegal drugs like those mentioned here, as well as legal drugs like alcohol and tobacco. You can continue reading about addiction in the article on smoking if you click here.

Cancer
The diagnosis of cancer always elicits our worse fears. There is probably no other medical disorder that produces such distress. And for one reason - cancer (we instinctively think) always means death. Sooner or later.
So, is that true?
First, let's discuss what cancer is.
All biological entities consist of cells, the smallest living biological unit. An average human adult male may have up to 36 trillion (36,000,000,000,000) cells.

Just to put that into context, our Milky Way galaxy, stretching out trillions of miles into space, is estimated to contain about 100 billion stars. That means that a human being contains over 300 times more cells than there are stars in our galaxy. That is simply amazing, especially considering how infinitesimally tiny a human being is compared to the Milky Way.
What is also amazing is that those 36 trillion cells grew exponentially from the two cells (one each from mother and father) that started you on the way to being human. That is the miracle of cell division, where one cell divides into two, then those two divide into four and so on. The study of cancer is all about cell division.

As you can imagine, cell division cannot go on forever. Complex interactions (signalling) occurs in the body to direct cell division. For example, if you get a cut, skin cells are stimulated to divide and heal the breach. As soon as that happens, a signal goes out to STOP. Do not divide any more.
Other cells, for example those in the stomach, intestine and bone marrow, go on dividing for life, but at a rate that replaces dead and worn out cells. All this is precisely programmed by signals that turn various genes on and off appropriately.
But like any complex structure, things can go wrong. The healthy cell will obey a stop-dividing signal until triggered again. However there are cells which very occasionally will refuse to obey a stop signal. These cells then go on dividing and dividing and dividing. These are rogue cells, defying the body's attempts at order.

The Immune System
But the body has an answer - the immune system. This is a system, also manned by millions of cells that continually circulate, looking out for anything that poses a threat to the body, like bacteria, viruses, fungi and other invading organisms. When they encounter such dangers, the immune system cells will usually surround and kill these invaders, often themselves dying in the process, but saving the body from further damage.
These same immune cells are also on the lookout for rogue cells and will kill them on contact, preventing them from doing more damage. When this system works - and it is always active without our being aware - then we are fit and healthy.
Sometimes however, the system fails and one rogue cell, or group of rogue cells manages to evade the immune system. This can happen when the immune system itself is weak, or when rogue cells successfully trick the system. You can see where this leads. These cells then hide in plain sight and, refusing to obey the body's legal commands, continue to divide and divide and divide....... A CANCER has started to grow. Cancer is the result of uninhibited cell growth in some organ.

How bad this is depends on the organ involved and the aggressiveness of the cell growth. Many cancers grow slowly and cause little serious damage. For example, skin cancers that result from sun damage do very little damage. Once removed, they usually do not pose any further threat for two good reasons. First, they are usually small; second, since they occur on the skin, they are easy both to spot and to remove.
Contrast this with a group of rogue brain cells. Locked inside the skull, these can grow for years without detection. Worse, having been detected, complete removal is challenging precisely because of where they develop. There are some parts of the brain you simply cannot get at, without causing major damage to healthy parts of the brain. The result is often a patient left severely crippled.

So, what causes cancer? Why do cells go rogue?
This question still haunts the medical experts, but increasintly answers are emerging. There are three main areas of interest.
Our own DNA
Everything about biology has to do with DNA - the code in every cell of our bodies that dictates what, who and how we are.
DNA consists of genes that dictate almost everything about the body. Throughout the long history of humanity, many genes have become damaged. The good thing is that, having inherited genes from both parents, the body can often switch off a bad gene inherited from one parent and use the good one from the other parent. But what if BOTH genes are damaged?
Damaged genes can lead to disease, including cancer. This is especially true for some varieties of breast cancer where inheritance of deranged genes plays a major part. It is the reason for the striking racial differences that exist in various disease profiles. Black men have more problems with prostate cancer than whites. On the other hand, white people have diseases like cystic fibrosis that are much less common in blacks. And so on.

The environment
The other major factor is our environment, both natural and man-altered.
Let's go back to skin cancer. We now know that many of these are caused by ultraviolet rays from the sun - a natural source. Long days sunbathing on the beach during the boiling midday sun, especially if you're white skinned, is very often the cause of skin cancer.
Then there is the damage that we have ourselves caused to our environment. This is a long list:
- Smoke pollution from industry
- Soil damage from pesticides, fertilizer and other chemical spills
- River, lake and sea pollution, also from industry
- Radiation damage - nuclear reactors especially
- Pollution of food sources - lead, DDT, micro-plastics etc
- Harmful processing of food
- War and its many awful legacies
- Climate change, itself a long list
There are myriad subtle interactions between the environment and our DNA that can lead to damaged genes. Our present knowledge only covers the tip of this iceberg.

Our Lifestyle
The third factor influencing cancer is our individual lifestyle. Arriving at firm data between lifestyle and disease is even more difficult. Lifestyles are often functions of culture, ethnicity, history, social norms and personal choices. But there are a few clear guidelines.
We know for sure that smoking tobacco can cause lung cancer, among other diseases. We also know that HPV (human papilloma virus) infection is very often the cause of cancer of the cervix in women. This virus is usually acquired through sexual contact, itself subject to varied behavioural practices.
We also know about the link between carcinogens in smoked and over cooked meats and some cases of colon cancer. Similarly radiation exposure is often implicated in bone and blood cancer. Marie Curie, who was a pioneer in discovering Xrays herself suffered this fate.
We also know that women who have never given birth are more at risk for breast cancer than those who have had children - an interesting finding.

Idiopathic
But the truth is that a large number of cancers fall into the idiopathic ("don't know") category. There are people who never smoke who contract lung cancer. Children with almost no life experience can develop kidney and eye cancer. We just don't know why.
So cancer is still a mystery in many ways.
Why is cancer so terrible?
As stated before, not all cancers are "terrible". But the defining behaviour that has given cancer its bad reputation is the ability to SPREAD to other organs.
The Spread of Cancer
Not all cancers spread. But the continued cell division typical of most cancers means that sooner or later, the number of cells grows so large that they begin to invade other organs.
So a cancer that begins in the nose, for example, can spread to the brain, a nearby organ. One that starts in bone can affect nearby muscles.
But the most aggressive action is when cells invade the vascular system - arteries, veins and lymphatics (another part of the vascular system). This allows cancer cells to spread essentially to any part of the body, no matter how distant. Prostate cells can invade the brain; breast cells can invade the liver. Malignant cells can go virtually anywhere blood goes. That is the main fear in most cancers - has it spread?
When doctors talk of stage 4 cancer, they are describing spread to many distant organs. This makes cure difficult, if not impossible, bacause of the limitations of medical treatment methods.
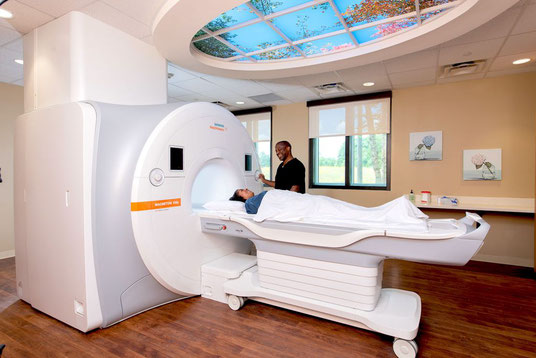
How is cancer treated?
Given the many different cancers, it is not possible to answer this in detail, but an overview will suffice.
The basic goal of cancer treatment is to remove from the body all malignant cells. If this can be done, then clearly there are no more cells to spread. The reason why early diagnosis is so advantageous is that cancers grow with time, so the earlier they are detected, the smaller they are and the more amenable they are to treatment. This is a general rule. Treatment then can be one, or more, of three methods.
Surgery
This aiims to physically remove (cut out) all cancerous tissue, or as much as possible. This is relatively easy in some locations like skin and bowel, but significantly more challenging in the brain or pancreas.
Radiation therapy
The surgeon's knife can only do so much. Radiation therapy is another method that doesn't remove cells but kills them in place using xrays. This can get at cells left over in location after surgery, or hiding nearby in lymph nodes. However the amount of radiation possible is limited because it can also kill normal healthy cells. Too much and the patient's life is in danger.
Chemotherapy
The great benefit of chemotherapy is that, like spreading cancer cells, it also travels via the blood stream. It can therefore hunt down cancer cells anywhere in the body that the blood system has taken them. Chemotherapy agents, like xrays, kill cells and can also harm normal tissue. It must therefore be given in strictly controlled doses and with careful monitoring.
The Good News
So, yes, a cancer diagnosis is usually seen as bad news, for the reasons given above. The good news however is that modern medicine has scored a number of significant successes in the treatment of many cancers.
Many cancers are now essentially curable with early diagnosis, including:
- some types of lymphoma
- breast cancer
- cancer of the cervix
- prostate cancer
- colon cancer
- ovarian cancer
- skin cancer
This is not an exhaustive list, the main factor influencing cure being early detection and a non-aggressive growth. This is the reason why so much of modern medicine focuses of regular screening.
For more information on a specific cancer which you may have worries about, contact your individual doctor.

Dementia
One of the most heart-wrenching experiences is to witness a previously smart, intelligent, kind, loving parent or close friend succumb to dementia. When the disease is full blown, the affected individual is completely helpless, usually speechless, unable to recognize anyone, unable to feed themselves, clothe themselves, bathe themselves or perform even the most trivial task without assistance. It is a truly devastating situation, especially for caregivers.
So what is dementia?
There are excellent online sources, including Wikipedia, that can provide a detailed description, so only a very brief resume is presented here.
The term dementia covers a wide range of conditions, but the underlying pathology in all conditions is loss of brain function, specifically memory, cognition (the ability to think), word skill and motor skill. What puts human beings apart from all other species is our large, complex and highly structured brains. When this gets damaged, essentially all our highly developed skills and capabilities suffer.
The most common form of dementia is Alzheimers disease, but there are other variants. As you well know, the brain is a highly complex arrangement of neurons. This structure gives us memory, both short and long-term, handles our emotions, supports speech and recall of words, and is the springboard for controlled and purposeful muscular activity. Dementia of all kinds damages the brain, eventually leading to failure of all high level behaviour.
Why is dementia common today?
That remains a mystery. The observed trends suggest that dementia is increasing in prevalence. In 2021 the number of people affected the world over was estimated at 55 million. This is expected to rise to 150 million by 2050. With better health generally, more people are living longer and the incidence of dementia does certainly increase with age, but age alone does not seem to explain the increase.
While a few specific causal relationships are recognized, the main causes are still not clear. What is known is that a number of abnormal proteins accumulate in the brains of people with dementia. These interfere with normal neural activity leading to the symptoms of dementia.
What can I do to avoid getting dementia?
Without knowing the actual cause or causes, the answer to that question is unknown. However, there are several recognized factors that are associated with a higher risk of succumbing to Alzheimer's disease and other dementias. A few are:
- A strong family history of dementia
- Parkinson's disease
- Heavy alcohol use
- Smoking
- Lack of exercise
- Lack of mental stimulation
- Depression
- Obesity
- Loneliness
- Increasing age
- Diabetes
Dementia may also follow some cases of HIV infection. Brain damage from severe head trauma will also increase the chances of dementia over time.
How can you treat dementia?
At the moment, there are no drugs known to cure dementia, though some preparations may effect some improvement in the patient's functional abilities temporarily. Treatment is basically looking after and supporting the affected individuals for the remainder of their lives. This can impose a massive burden on family members, especially elderly wives and husbands who have themselves limited physical capacities. All effort should be made to provide a stimulating environment where the patient is challenged to use his/her remaining capacities for as long as possible.
Following this principle, in some parts of the world, small businesses have sprung up which actually employ people with early dementia as waiters/waitresses. The aim is to keep them active and engage their minds in problem solving as long as possible. This has been met with public acclaim.

In summary
Dementia is now a worldwide crisis and appears set to increase in prevalence. While no effective treatment is currently known, given the risk factors mentioned above, it would seem sensible to:
- Stay as young as long as possible!!
- Avoid alcohol
- Don't smoke
- Maintain your proper weight
- Exercise regularly
- Eat well, avoiding highly processed foods
- Get enough sleep
- Maintain healthy social relationships
- Challenge your mind constantly (word puzzles, music etc)
- Learn to laugh and enjoy life
This may not save you from getting dementia, but at least you would have tried your best. Once you do that, well, angels can't do better, they say!

Heart Attack
Medically called a myocardial infarction, heart attacks are one of the commonest killers worldwide, with nearly twice as many men affected compared with females.
As is now commonly known, heart attacks occur when part of the heart muscle loses its blood supply. The heart, given its never-ending task of pumping blood all around the miles of blood vessels, has a heavy and continuous demand for blood itself. Any time the supply of blood to the heart suffers, there is the potential for serious trouble.
The first symptom is usually chest pain, called angina. This may occur weeks to months before an actual attack. Many people will pass off these warning signs as indigestion or, as is only too common in Barbados, "gas" pains.
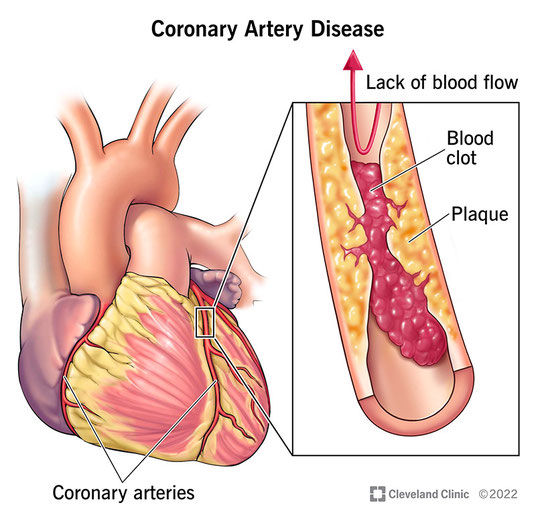
Why do arteries stop working?
Arteries are responsible for transporting blood all over the body. Because of the fairly high pressure put out by the pumping heart, the walls of arteries are muscular and strong and can react to changes in pressure by contracting (making the lumen smaller) or dilating (making it wider).
In the healthy individual, the internal walls of arteries are clean. In other persons, a number of fatty compounds can build up on these internal walls, reducing the blood flow. This is called plague. As this process continues, less and less blood can traverse the narrow space. This is when the first symptoms tend to occur, with chest pain (angina) occurring during heavy physical activity.
In time, blood flow can be reduced to the point where muscle is impaired and may actually die. This is a heart attack (myocardial infarction). As well as plaque formation, sudden spasm in the artery can cause similar symptoms. Another cause of blocked arteries is a clot or thrombus.
In this scenario, clots form in the heart itself or at other locations. Parts of an unstable clot can then break off and travel to the heart where they can obstruct an artery, leading to the same symptoms.

So what is responsible for plaques and clots?
The pathology of heart disease is now well established. The major drivers are:
- Hypertension (high blood pressure)
- Diabetes
- Smoking
- Obesity
- Lack of exercise
- High cholesterol
You would recognize all the above as the well known elements of non-communicable disease (NCDs), against which the entire world is now fighting. Despite excellent information, large numbers of people, including young children, still gorge on low quality fast food, will not exercise, consume too much fatty food, binge on alcohol and smoke (cigarettes, marijuana, vaping). The end result is a large segment of the population that is overweight, hypertensive, diabetic and lazy, with elevated cholesterol levels. This is cannon fodder for heart attacks.

What about survival after an attack?
Few people survive a massive heart attack. In such situations, so much of the heart muscle dies (due to several arteries being affected), that the heart is simply unable to work. Death follows.
A greater number of heart attack victims make it to hospital. With prompt care, a majority of these will recover. How long they survive after the first (or subsequent) attack will depend on a list of factors including:
- how much damage the heart has suffered
- how well their hypertension is managed
- whether they are overweight
- or diabetic
- and how compliant they are with medical advice
What can I do to avoid a heart attack?
Whether you avoid a heart attack or not depends on a large number of variables, including genetic factors beyond your control. However there are a large number of things within your control. This constitutes your lifestyle and is a powerful determinant of your present and future health. Many of these are now well known:
- Weight control and avoidance of obesity
- Regular and consistent exercise
- Healthy diet
- Avoidance of alcohol and smoking
- Adequate sleep
- Good mental health
- Compliance with medication regimes if you are diabetic or hypertensive
On the other hand, some people reason that life is too short to concern themselves with so many rules and restrictions. Eat, drink and be merry, they say, for tomorrow you die. And generally, they do. The choice is yours, which path you follow. Either way, there is a price to pay.

You almost never think about your kidneys.
Why should you? Sure, you know they're there, somewhere in your back. And you know they produce urine. That's about it. You never see them. Generally they never complain. So.....
What more is there to know?
For starters, they are vital for life. You can't live without them. Like so many biological organs, kidneys are fascinating. Let's take a brief look at them.
What exactly are kidneys?
Kidneys of some sort are found in all biological entities, for one major reason. They help maintain the internal environment in a state compatible with life. Consider a typical day in your life. You eat what you like, drink what you like and as much as you like. You have absolutely no idea, nor could you care less, how much sodium or potassium or chloride or magnesium was in that beef and potato roti.
But here's the problem. Life is a chemical tight-rope that demands very narrow tolerances of many substances that abound in nature. Too much, or too little of many common chemicals, and life dies. The roti you just ate is a dizzying mixture of water, various acids, alkalis, and a whole slew of other chemicals like zinc, iron, magnesium, sodium, potassium, and more. Without kidneys, your blood, as well as the fluid that nourishes every cell in your body would soon begin to resemble roti juice, with way too much salt than life requires. In just over a week, you'd be dead - brain and heart cells clogged with salt and probably hundreds of other unwanted chemicals.

What has kept you alive is your kidneys. Half an hour after you finished the roti, your kidneys (which receive nearly a quarter of all blood pumped by the heart), started to detect a rise in salt levels beyond what is good for you.
They also detected a change in your acid-base balance, also crucial for life. Intelligent nephrons (kidney cells) then got to work. Using a battery of inter-nephron signalling, they began to extract from the blood circulating through the kidneys all the excess salt (sodium and chloride) that you just consumed. They also noted that slight increase in acidity from the beef and adjusted the hydrogen ion concentration in the urine so that your body fluids remain at the optimum pH value.
All that, without breaking a sweat. Within reason, you can eat what you want, drink what you like, and as much as you like, without worry. Your kidneys do the heavy lifting - adjusting fluid balance, titrating body pH, and maintaining critical levels of hundreds of chemicals that are essential for life. If you take in too much, the kidneys get rid of the excess in the urine. If you take in too little, they restrict the amount in the urine to restore balance. And they do this day and night, every second. They never take vacation. Never go on leave. Never take a break. And never complain. Well...... almost never.

What do you mean --- almost never?
Because kidneys can become diseased. Everybody has heard about kidney stones. These are literally small stones (yes, like the ones in your yard) that develop within kidneys and can cause severe pain if they block the ureter (which brings urine from the kidneys to the bladder).
But what many people don't know is that kidneys can fail. It is common knowledge that the heart can fail - heart failure. We know too that the liver can fail - liver failure, often the result of drinking too much rum for years. But kidney failure is not something many people are familiar with.
So what is kidney failure?
Kidneys are said to fail when they stop their critical work of protecting the body's internal environment. Going back to the roti discussion, no longer would failed kidneys get rid of excess salt. Nor would they make any attempt to correct the increase in acidity from the meat you ate. What happens in kidney failure is that slowly, inexorably, the body gets swamped by toxic levels of salt, water, potassium, and hundreds of other chemicals taken in in foods and medicines, as well as those released by normal cell death. Eventually the brain , heart and other vital organs can no longer work. You are in the valley of death.

What causes kidneys to fail?
Because we have two kidneys, and can survive quite well on only one, most people will never have kidney failure. The most significant cause(s) of kidney failure are diabetes and hypertension, alone or in combination. Both diabetes and hypertension adversely affect the small blood vessels in many organs, including kidneys.
The nephron (kidney cell) can only do its job when its associated blood vessel (the glomerulus) is healthy. When the latter gets damaged by long-standing diabetes or poorly controlled blood pressure, the kidney is in trouble.
As you age, like every other organ, the kidneys lose some of their competence. They may then not be able to perform at the optimum level, but this is not failure. They can still do their job of regulating and excreting various elements, though not as aggressively as in the past. At this stage there are no symptoms and life goes on, though various blood and urine tests will show the deficiency.
Kidney failure, or to give it its full description, end-stage kidney disease, occurs when the kidneys are no longer able to do their job. Even here, there are levels of failure. However eventually, with time in many cases, failure is complete.

Then what? Can it be treated?
There are basically only two ways to treat complete kidney failure:
- Dialysis
- Kidney transplant
A successful kidney transplant is the ideal treatment. Except for drugs to discourage rejection of the organ, life can go on as before. But getting a transplant is not easy. The first problem is finding a compatible donor. For identical twins, this is easy. Most people however don't have a twin. And many third world countries simply cannot afford the expense of transplant surgery.
This leaves dialysis as the other option. In dialysis, an artificial machine mimics the work of the kidney. For a couple of hours, two or three times a week, the patient is hooked up to a device that takes the patient's blood and circulates it through a series of membranes that remove the accumulated toxins. While not nearly as efficient as healthy kidneys, it does get the job done and patients can live for decades on dialysis. But as you can imagine, having to go into a centre three times every week without fail, is a major life-style change.
What can I do to prevent kidney failure?
As with many things in life, you can only do your best. Whether this helps you avoid kidney failure is anyone's guess. Some people develop kidney disease through no fault of their own. Many times, it is the final legacy of long-standing diabetes and hypertension. But it can follow other conditions like lupus, trauma, infections, drug effects, congenital kidney states and more. But your best shot, as with nearly all medical conditions, would be to:
- Avoid smoking
- Avoid alcohol
- Get plenty of exercise
- Avoid obesity
- Eat as healthily as you can
- Be happy

"No way, not interested"
That's how some people respond when offered conventional medical treatments. For example, a woman goes to her doctor with an infection and the doctor suggests a course of antibiotics. "No way", she says.
Or, a biopsy of a lump in the breast comes back as cancer. "We need to operate", says the doctor. The lady shakes her head vehemently. "No surgery. No radiation. No chemotherapy".
"Well, what are you going to do?", asks the doctor, baffled. "I am going to see my homeopath for natural medicine", is the reply.
So, what really is natural medicine?
Let me say, up front, that this article reflects my personal opinion and is frankly biased. It is based on years of seeing patients suffer unnecessary pain and distress, and in some cases, death, from a misplaced faith in non-conventional health remedies.
Before I answer the question, let me explain what conventional medicine is.

Hundreds of years ago, before the age of science, philosophers ruled the day. Men would sit and think up answers to the many problems they faced, from bad weather, to horrible plagues, to common sicknesses. With no knowledge of basic science, they dreamed up various concepts. One such was that all nature was made up of Earth, Wind, Fire and Water. Another was that disease was due to "bad air", from which we get malaria (mal and aria). Another concept was that of ether.
In medicine these notions led to practices like blood-letting to cure disease. The truth was - all this was based on wild notions without any foundation. And you can't blame them - they did the best that they could.

Things began to change from about the time of Sir Isaac Newton (17th Century) whose publication of Mathematical Principles of Natural Philosophy initiated a groundswell of scientific revolution. No longer was it okay to just dream up interesting but unproveable theories. One could now do scientific experiments in which theories could be proved or disproved.
It was during this revolution that the telescope was born, as was the printing press. Ideas could now be published and either proved or disproved by anyone, in any country. The mysterious nature of light was investigated, electricity was discovered. So were radio waves and xrays. Alexander Graham Bell invented the telephone. Television soon followed. Researchers at the Bell Labs created the transistor in 1947-8.
The nature of matter was found to be considerably more complex than Neils Bohr had suggested in his model of the atom. Edwin Hubble found new mysteries in the universe that were hitherto unknown. Knowledge was expanding at a dizzying pace. Long gone were the murky mysteries of the past. This was the age of science.

While Hippocrates who lived 2400 years ago is still described as the father of modern medicine, it was really people like William Harvey, pictured here, who discovered the circulation of the blood, that set the foundation for modern scientific medicine. Intrepid doctors, battling entrenched taboos, were now able to do dissections of cadavers, setting the stage for sound anatomical foundations.
In 1846, ether, the first anaesthetic agent was used on a patient. In 1928 Alexander Fleming discovered the very first antibiotic, penicillin, still widely used today. Various wars in the 20th Century, horrible though they were, galvanized advances in surgery and trauma medicine. Other antibiotics were soon created to treat various bacteria (these were known since the 1600's).
With all the foregoing as a solid foundation, modern medicine firmly belongs to the 20th Century. Sophisticated Xray machines, CT scans, MRI and PET scan machines can now image the entire human body in real time. The precise nature of DNA and cell biology, including fine details of biochemical mechanisms have been worked out and published. Drugs are now designed to specifically target individual diseases. Modern medicine is now fully scientific.

So are you saying medicine knows everything?
Not at all. The human body is so complex that in another million years of leaning, we still will not know all that there is to know.
But one thing is dead certain. The human body (and mind) are based on sound laws of physics, chemistry and biology. Any discipline that purports to treat disease successfully, must also be based on sound science, not myth and hocus-pocus. That is why conventional medicine has been so successful in explaining and treating disease. And that is why I have faith in modern scientific medicine, while at the same time appreciating that there are limits to what medicine knows and can do.

So, back to homeopathic and naturopathic treatments.
Any treatment plan that is not soundly based on known medical science - anatomy, physiology, biochemistry etc - to my mind is doomed to fail.
But, it works!!
Many people will say, quite truthfully, that they went to such and such a homeopath or naturopath or chiropractor and got better. I have no doubt that this is true. Many physical ailments have a natural life history. The body can indeed heal itself from many maladies in time, whether treated or not. So many disorders and diseases will correct themselves in time, no matter what you do (provided that what you do does not worsen the condition).
However, there are some diseases and medical conditions that are so severe that the body generally is incapable of self-healing. If you fall and break a hip, acupuncture will not correct it. Neither will a bottle of green water from a naturopath.
When your pancreas fails and you become diabetic, no chiropractor's spinal manipulation will cure your elevated blood sugar. If that lump in your breast is indeed cancer, homeopathy is of no use to you whatsoever. Indeed, there are many disease conditions where even conventional medicine will fail.
I can clearly recall admitting a lady to hospital as a junior doctor, straight from her chiropractor's office. She had consulted the practitioner because of a common ailment - back pain. The treatment consisted of being placed on some sort of contraption to stretch the aching back. The result was a broken back and paralysis. That is a true story.
I also know personally of patients diagnosed with breast cancer who refused conventional treatment in favour of homeopathic promises of cure. When they finally came back, after months of disillusionment, they were beyond any meaningful treatment, with masses of cancerous tissue fungating through the chest wall and pouring pus.

So, you've been warned.
Still, it's your body. It's your call. But remember, health is not based on dodgy notions but sound laws of nature.

Dealing with death
From the very moment life appeared on earth, death has been present. Yet, we never get used to it. While modern funerals always strive to "celebrate" the life of the deceased, nothing can take away the sense of loss, the absolute tragedy, the awful sadness that death brings in its wake. Death is the very antithesis of life. And it is forever.
What really is death?
This is not as silly a question as it sounds. In days of yore, before modern medicine, when you died, you were....well, dead. Today, people can be kept for months on life-support in a state that makes definition of death - or life - difficult.
Under natural conditions, once circulation and breathing stops, cells soon begin to die. This is easy to understand. For cells to survive, they must be supplied with nutrients and oxygen. When this supply is cut off, after a variable time, the cell dies. But the cells in different organs have different tolerances for nutritional and oxygen starvation. The most sensitive are brain cells.
Because of its highly specialized function, the brain cannot tolerate, on average, more that about 4 minutes of oxygen lack. This is how strangulation works. Excessive pressure on the neck will stop circulation to the brain; if this is maintained for 3-4 minutes, death ensues from irreversible brain damage.
But other cells in the body. like those of muscle, skin and bone, can survive for much longer without oxygen. While performing orthopedic operations, the surgeon routinely uses a tourniquet to cut off blood supply to part of a limb for more than 30 minutes with no subsequent loss of function. Doing this permits surgery to be performed without blood getting into the surgical field.
With modern life support capabilities, it is common for severely injured patients to be kept alive for months without any sign of brain activity while the heart continues to beat. In the past, such an individual would have died within minutes. This often leads to the agonizing situations you hear about when decisions have to be made to take the patient off life support and allow nature to run its course. However when the heart stops, unless it can be restarted within a short time, death is certain. A functioning circulation is absolutely required for life. So is oxygenation; if there is no breathing - either natural or assisted - life cannot continue.
In summary then, death is final when there is no circulation, no breathing and no brain activity.

Is it true that people can come back from the dead?
Stories now abound about people who "come back" from the dead. The general notion is that the person "died", saw themselves floating above their sick bodies, could hear conversations around them, and then went back into their bodies.
Given the absolute finality of death, it should be clear that nobody can die and come back. The more correct term might be near-death experience. Very ill people may indeed report very strange phenomena, including "out-of-body" experiences. They certainly can be near death and recover. But death, properly defined, is final. Once the brain is completely dead, the heart stops and there is general cell death, there is no coming back. At least not without a true miracle.

Is death inevitable?
Yes.....but maybe not. Common human experience says that we all will die. And not only humans, but all life forms eventually succumb to death. Life is fleeting.
But recent discoveries at the cellular level have cast a totally different light on this subject.
It has been found that for cell death to occur, certain genes have to be switched on in the cell's DNA. When this happens, the cell begins the process of dying. If these genes are not activated, the cell tends to go on living.....and living....and living. This strange development is seen especially clearly in certain strains of cancer cells that simply refuse to die. This has given scientists hope that one day, it might be possible to prevent - or at least, significantly delay - death. If one could find a way to keep these death genes from switching on, it might not be far-fetched to conceive of eternal life. But you shouldn't hold your breath that this will happen any time soon.
Is death painful?
What many of us fear it not death itself, but the pain and loss of dignity that can accompany dying. We hear stories of people "losing the battle" with cancer or some other dreaded disease. We know that they generally suffer the pain of disease, the discomfort of chemotherapy, the indignity of illness and a hundred other infelicities before the actual time of death. And that is what we fear.
But death itself is generally not at all painful. Most people who die simply go to sleep. It is more than likely that there is a sort of death program in the brain that acts like a heavy dose of morphine, making the dying more or less unaware of acute physical suffering. Especially when death results from acute trauma like motor vehicle accidents, one can usually say for certain that the person did not suffer. In such cases there is usually no time for the brain to register any pain. It is commonplace for individuals who get shot, and survive, to relate that they were not even aware that they were shot.
This knowledge can give relatives a great deal of comfort - to know that very often their deceased loved ones did not suffer as much as one would think.

So, death is our final appointment. It will come sooner or later. We get one chance at this wonderful but fleeting thing called life.
Why waste it?
Why not make full use of it?
Why waste time fretting and grumbling?
Why spend so much time worrying about things we can't change?
Why not instead enjoy life?
Why not make the most of it?
It's never going to be perfect, but it sure can be very good.
